MySQL中的EXPLAIN用法及解读
13人参与 • 2025-07-21 • Mysql
一、介绍
官网介绍:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/explain-output.html
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/explain-output.html
explain(执行计划),使用explain关键字可以模拟优化器执行sql查询语句,从而知道mysql是如何处理sql语句。
explain主要用于分析查询语句或表结构的性能瓶颈。
通过explain命令可以得到:
- – 表的读取顺序
- – 数据读取操作的操作类型
- – 哪些索引可以使用
- – 哪些索引被实际使用
- – 表之间的引用
- – 每张表有多少行被优化器查询
explain 或者 desc命令获取 mysql 如何执行 select 语句的信息,包括在 select 语句执行过程中表如何连接和连接的顺序。
版本情况:
- mysql 5.6.3以前只能explain select ;mysql 5.6.3以后就可以explain select,update,delete
- 在5.7以前的版本中,想要显示partitions 需要使用explain partitions 命令;想要显示filtered 需要使用explain extended 命令。在5.7版本后,默认explain直接显示partitions和filtered中的信息。

基本语法:
explain 或 describe语句的语法形式如下:
explain select select_options
或者
describe select select_options
环境准备:
create database testexplain character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_general_ci;
use testexplain;
create table l1(id int primary key auto_increment,title varchar(100) ); create table l2(id int primary key auto_increment,title varchar(100) ); create table l3(id int primary key auto_increment,title varchar(100) ); create table l4(id int primary key auto_increment,title varchar(100) );
insert into l1(title) values('test001'),('test002'),('test003');
insert into l2(title) values('test004'),('test005'),('test006');
insert into l3(title) values('test007'),('test008'),('test009');
insert into l4(title) values('test010'),('test011'),('test012');
二、基本的使用
explain使用:explain/desc+sql语句,通过执行explain可以获得sql语句执行的相关信息。
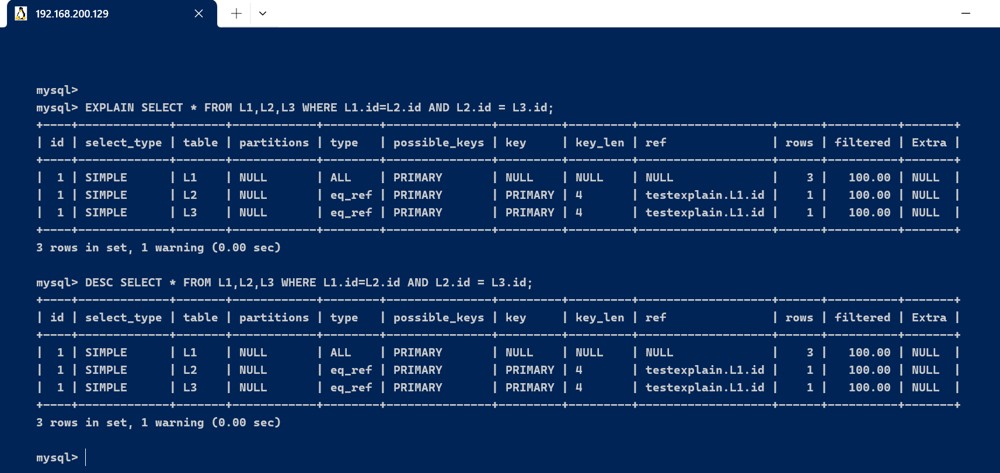
explain select * from l1,l2,l3 where l1.id=l2.id and l2.id = l3.id; desc select * from l1,l2,l3 where l1.id=l2.id and l2.id = l3.id;
| 序号 | 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | id | 查询的序列号,是一组数字,表示查询中执行 select 子句或操作表的顺序。 |
| 2 | select_type | 表示 select 的类型。常见取值有 simple(简单查询,不包含子查询或联合查询)、primary(主查询,即最外层的查询)、union(联合查询中的第二个或后续查询)、subquery(子查询)等。 |
| 3 | table | 表示正在访问的表。 |
| 4 | partitions | 显示匹配的分区信息,如果是非分区表则为 null。 |
| 5 | type | 表示表的访问类型,性能由好到差的顺序为 system → const → eq_ref → ref → ref_or_null → index_merge → unique_subquery → index_subquery → range → index → all。访问类型越靠前,性能越好。 |
| 6 | possible_keys | 表示查询时可能使用的索引。 |
| 7 | key | 实际使用的索引。如果没有使用索引,则显示为 null。 |
| 8 | key_len | 表示使用的索引的字节数。这个值越大,表示查询中使用的索引字段越多。 |
| 9 | ref | 显示索引的哪一列被用到,并且如果可能的话,是哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列中的值。 |
| 10 | rows | 估计要读取的行数,这个数字是一个估计值,不一定是精确的。 |
| 11 | filtered | 表示服务器根据查询条件过滤的行百分比。 |
| 12 | extra | 包含执行查询的额外信息,比如是否使用临时表、是否进行文件排序等。常见值有 using index(使用了覆盖索引)、using where(使用了 where 过滤条件)、using temporary(使用了临时表)和 using filesort(使用了文件排序)等。 |
三、字段详解
3.1、id字段
select查询的序列号,包含一组数字,表示查询中执行select子句或操作表的顺序
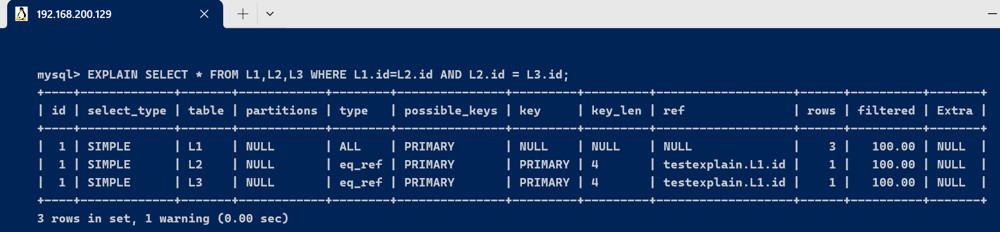
- id相同,执行顺序由上至下
explain select * from l1,l2,l3 where l1.id=l2.id and l2.id = l3.id;
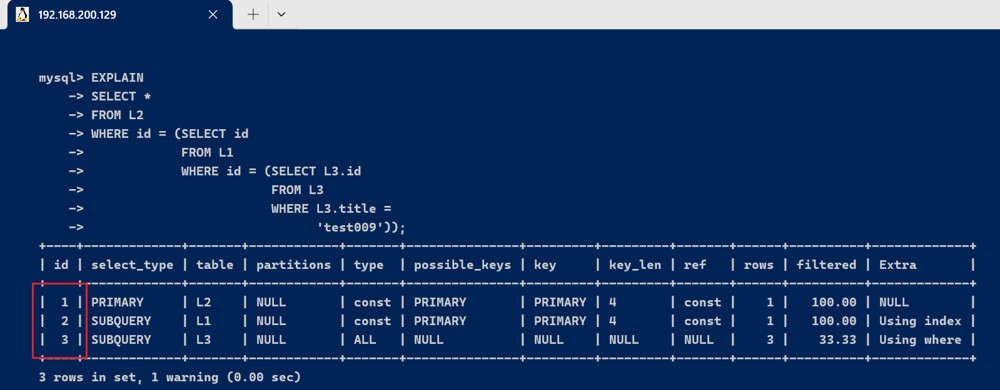
- id不同,如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id值越大优先级越高,越先被执行
explain
select *
from l2
where id = (select id
from l1
where id = (select l3.id
from l3
where l3.title =
'test009'));
3.2、select_type 与 table字段
查询类型,主要用于区别普通查询,联合查询,子查询等的复杂查询
- simple : 简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或者union
explain select * from l1;
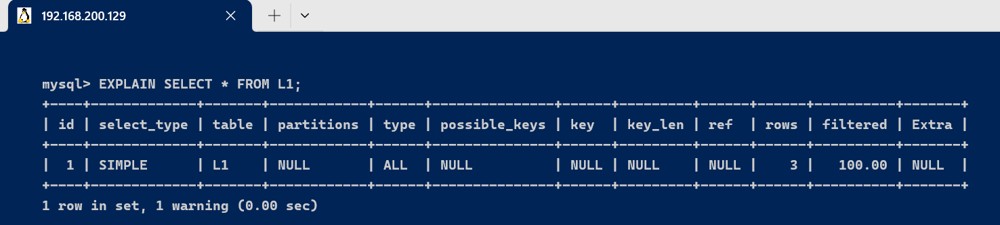
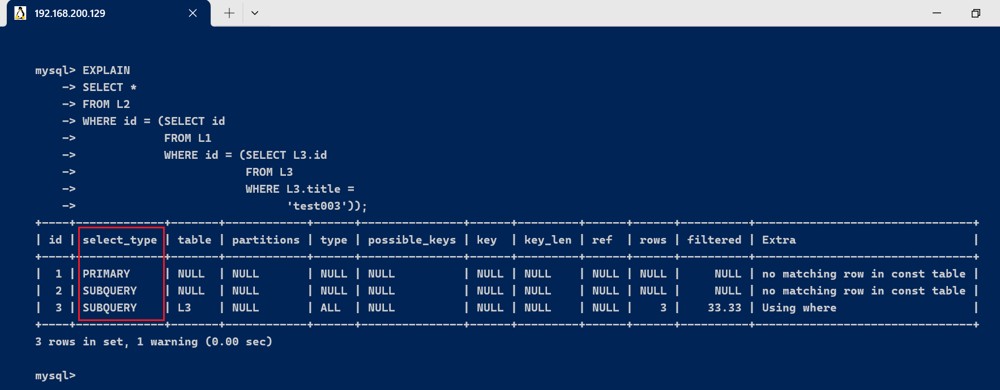
- primary : 查询中若包含任何复杂的子部分,最外层查询被标记
explain
select *
from l2
where id = (select id
from l1
where id = (select l3.id
from l3
where l3.title =
'test003'));
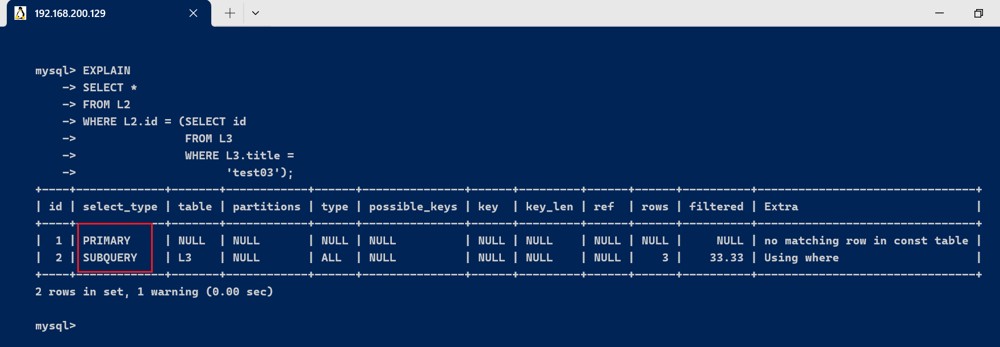
- subquery : 在select或where列表中包含了子查询
explain
select *
from l2
where l2.id = (select id
from l3
where l3.title =
'test03');
- derived : 在from列表中包含的子查询被标记为derived(衍生),mysql会递归执行这些子查询,把结果放到临时表中
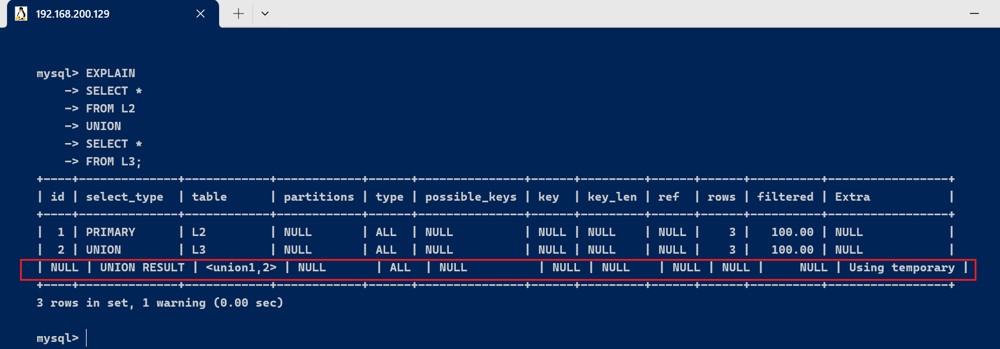
- union : 如果第二个select出现在union之后,则被标记为union,如果union包含在from子句的子查询中,外层select被标记为derived
- union result : union 的结果
explain select * from l2 union select * from l3;
3.3、partitions
分区表是将一个表的数据根据某个字段的值分成多个分区来存储的,这样查询时可以提高效率。
查询时匹配到的分区信息,对于非分区表值为null ,当查询的是分区表时, partitions 显示分区表命中的分区情况。
对于非分区表(例如原始的 l1 表),partitions 字段会显示 null:
explain select * from l1 where id = 1;
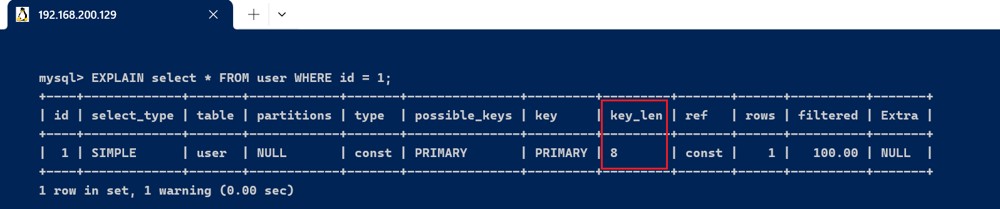
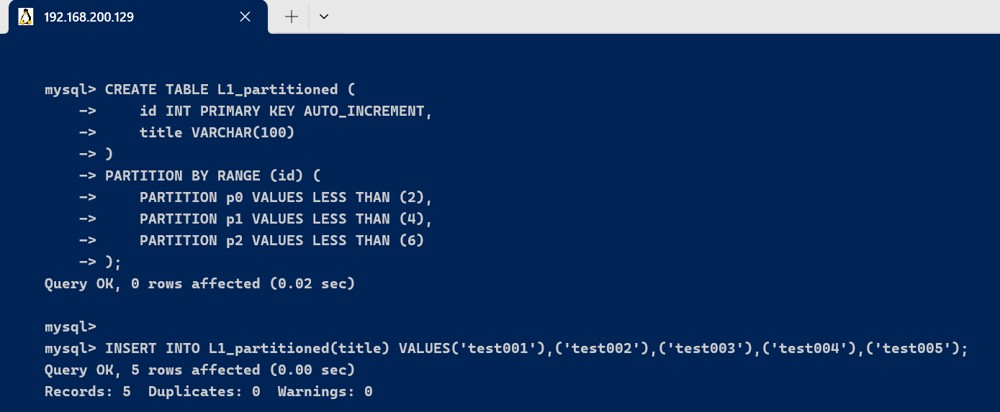
我们以 l1 表为例,将它根据 id 字段进行分区:
create table l1_partitioned (
id int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(100)
)
partition by range (id) (
partition p0 values less than (2),
partition p1 values less than (4),
partition p2 values less than (6)
);
insert into l1_partitioned(title) values('test001'),('test002'),('test003'),('test004'),('test005');
这个表会根据 id 的值分成 3 个分区:
p0分区存储id小于 2 的数据p1分区存储id小于 4 的数据p2分区存储id小于 6 的数据
使用 explain 查看查询的分区命中情况:
explain select * from l1_partitioned where id = 1;
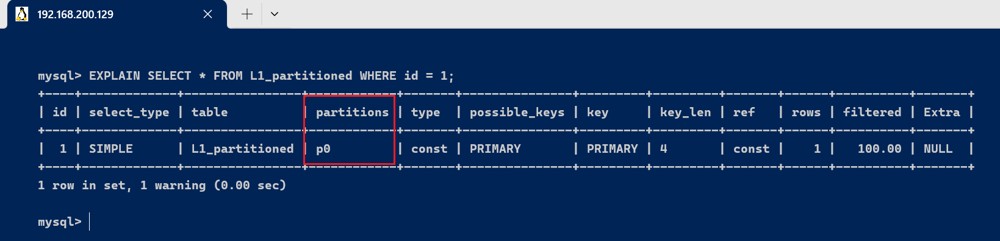
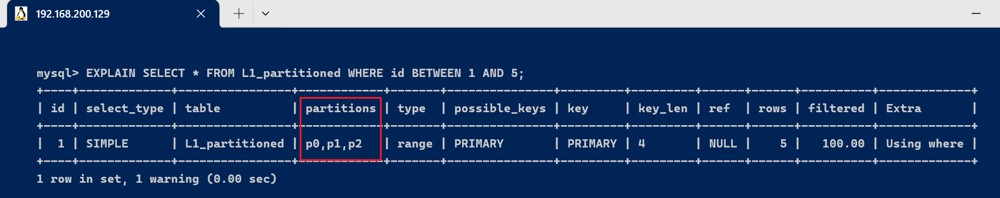
此查询会显示 partitions 字段的值为 p0,因为 id=1 的记录被存储在 p0 分区中。
explain select * from l1_partitioned where id = 3;
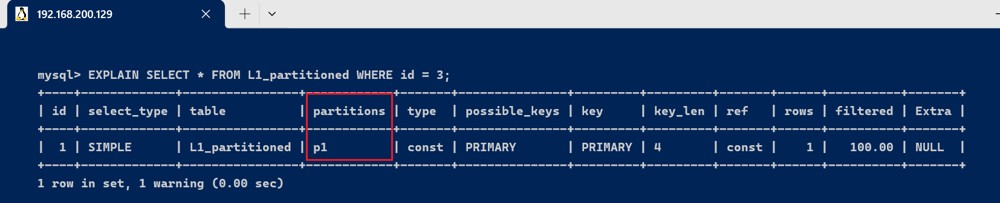
此查询会显示 partitions 字段的值为 p1,因为 id=3 的记录被存储在 p1 分区中。
当查询条件跨越多个分区时,explain 会显示命中的多个分区:
explain select * from l1_partitioned where id between 1 and 5;
3.4、type字段
type显示的是连接类型,是较为重要的一个指标。
下面给出各种连接类型,按照从最佳类型到最坏类型进行排序:
system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge >unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > all
-- 简化
system > const > eq_ref > ref > range > index > all
- system : 表仅有一行 (等于系统表)。这是const连接类型的一个特例,很少出现。
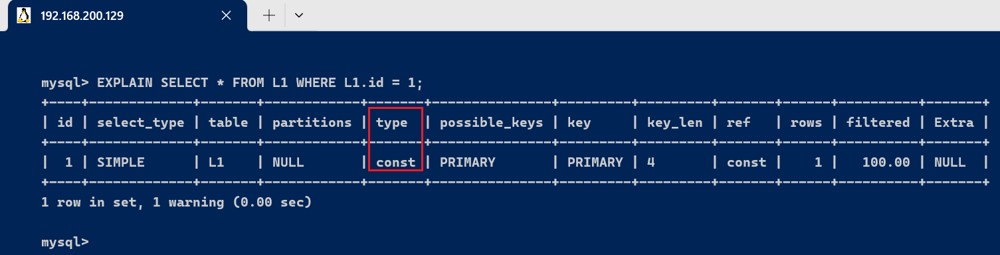
- const : 表示通过索引 一次就找到了, const用于比较 primary key 或者 unique 索引. 因为只匹配一行数据,所以如果将主键 放在 where条件中, mysql就能将该查询转换为一个常量
explain select * from l1 where l1.id = 1;
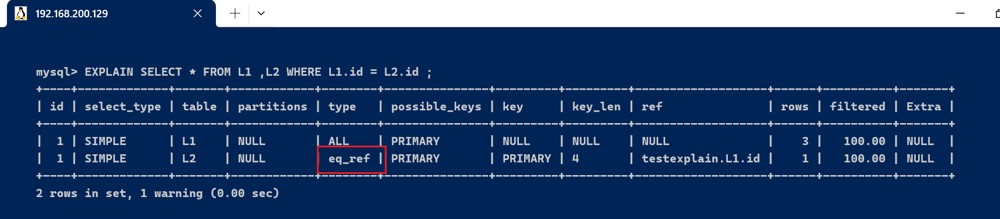
- eq_ref : 唯一性索引扫描,对于每个索引键,表中只有一条记录与之匹配. 常见与主键或唯一索引扫描
explain select * from l1 ,l2 where l1.id = l2.id ;
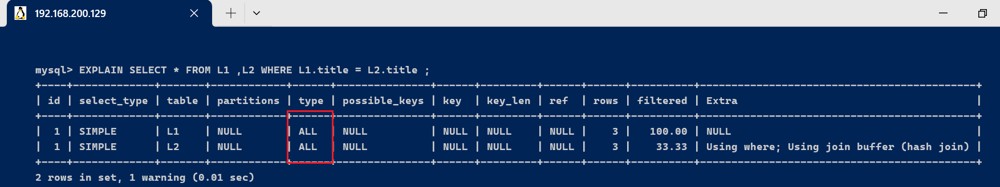
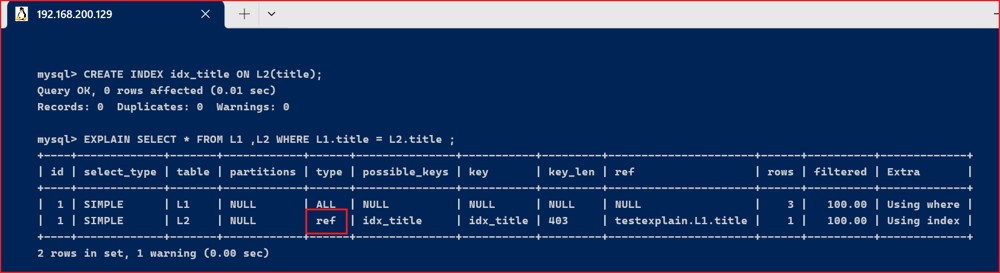
ref : 非唯一性索引扫描, 返回匹配某个单独值的所有行, 本质上也是一种索引访问, 它返回所有匹配某个单独值的行, 这是比较常见连接类型.
- 未加索引之前
explain select * from l1 ,l2 where l1.title = l2.title ;
- 加索引之后
create index idx_title on l2(title);
explain select * from l1 ,l2 where l1.title = l2.title ;
- range : 只检索给定范围的行,使用一个索引来选择行。
explain select * from l1 where l1.id > 10;
explain select * from l1 where l1.id in (1,2);
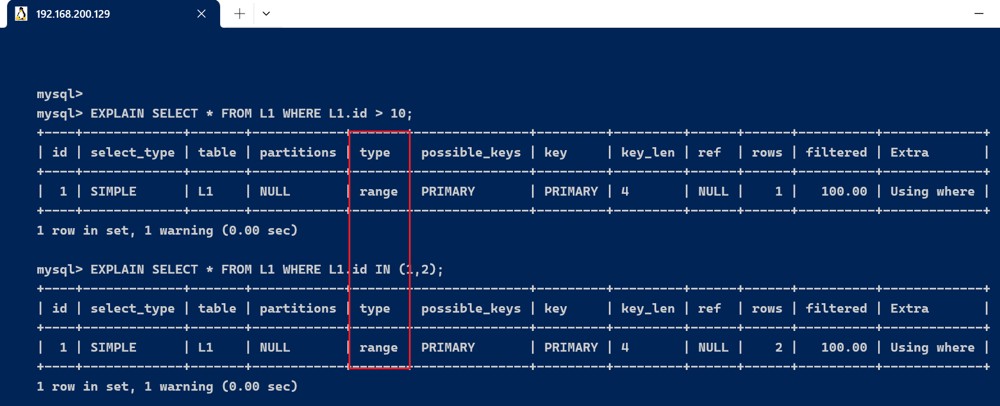
key显示使用了哪个索引. where 子句后面 使用 between 、< 、> 、in 等查询, 这种范围查询要比全表扫描好
index : 出现index 是 sql 使用了索引, 但是没有通过索引进行过滤,一般是使用了索引进行排序分组
explain select * from l1 order by id;

- all : 对于每个来自于先前的表的行组合,进行完整的表扫描。
explain select * from l1;
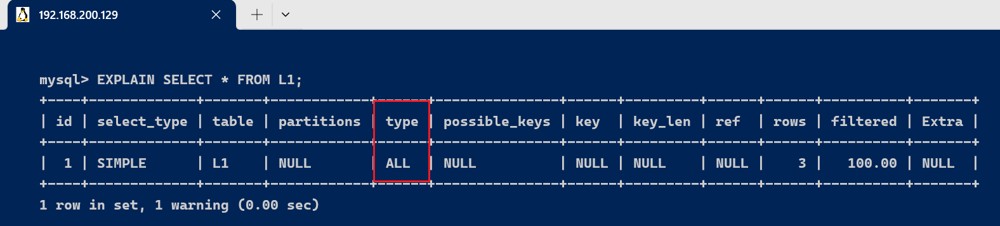
一般来说,需要保证查询至少达到 range级别,最好能到ref
3.5、possible_keys 与 key字段
possible_keys
- 显示可能应用到这张表上的索引, 一个或者多个. 查询涉及到的字段上若存在索引, 则该索引将被列出, 但不一定被查询实际使用.
- 实际使用的索引,若为null,则没有使用到索引。(两种可能,1.没建立索引, 2.建立索引,但索引失效)。查询中若使用了覆盖索引,则该索引仅出现在key列表中。
key
- 实际使用的索引,若为null,则没有使用到索引。(两种可能,1.没建立索引, 2.建立索引,但索引失效)。查询中若使用了覆盖索引,则该索引仅出现在key列表中。
- 覆盖索引:一个索引包含(或覆盖)所有需要查询的字段的值,通过查询索引就可以获取到字段值
理论上没有使用索引,但实际上使用了
explain select l1.id from l1;
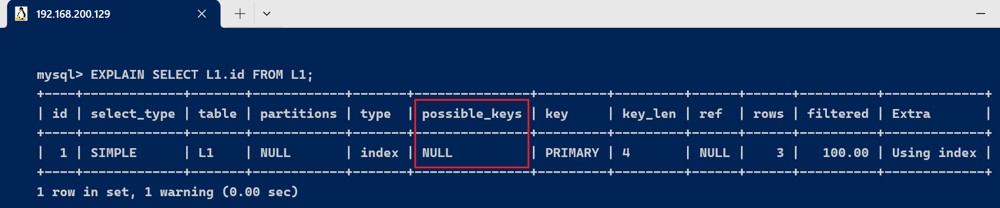
理论和实际上都没有使用索引
explain select * from l1 where title = 'test01';
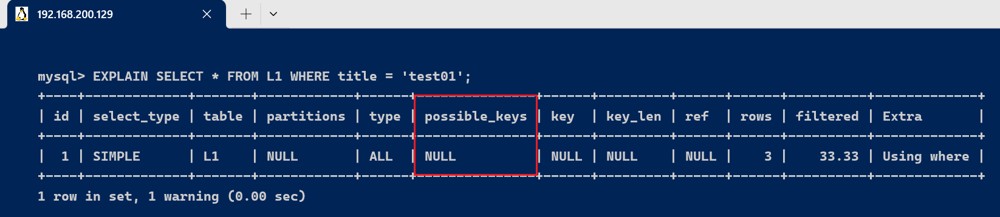
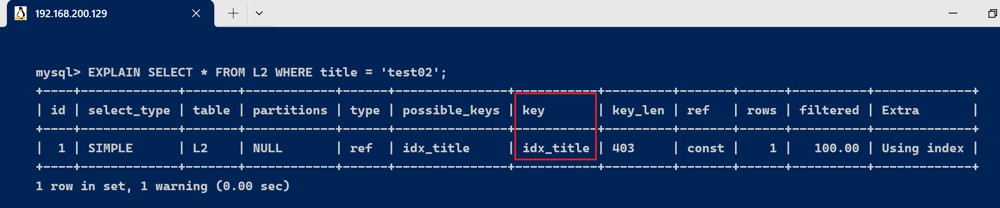
理论和实际上都使用了索引
explain select * from l2 where title = 'test02';
3.6、key_len字段
表示索引中使用的字节数, 可以通过该列计算查询中使用索引的长度.
key_len 字段能够帮你检查是否充分利用了索引 ken_len 越长, 说明索引使用的越充分
key_len表示使用的索引长度,key_len可以衡量索引的好坏,key_len越小 索引效果越好
上述的这两句话是否存在矛盾呢,我们该怎么理解呢?
第一句:key_len 越长,说明索引使用得越充分
解释:
key_len表示在查询中使用的索引字节数。它反映了查询条件中实际使用了索引的多少。- 例如,假设有一个复合索引(例如
index_a_b_c),它包含三个字段a, b, c。如果你执行的查询只使用了a字段进行筛选,那么key_len可能只包含字段a的长度。如果查询使用了a和b两个字段进行筛选,key_len会增加,以反映更多的索引字段被使用。 - 因此,当
key_len较长时,意味着查询充分利用了索引的多个部分,这通常可以提高查询效率。
第二句:key_len 越小,索引效果越好
解释:
- 这句话强调了索引的选择性和效率。
key_len越小,表示查询使用的索引部分越少,也可能意味着查询的目标更加精准,过滤的行数越少。 - 如果一个查询只需使用索引的前几列(即
key_len较小),并且可以快速过滤掉大部分不相关的行,那么该查询的效率通常会更高。 - 在某些情况下,使用较小的
key_len可能会比使用较大的key_len更有效,因为这减少了不必要的索引扫描(特别是当大部分行都匹配前面的字段时)。
如何综合理解这两句话
这两句话并不矛盾,而是从不同的角度解释了 key_len 的作用:
- 充分利用索引:当你希望尽可能利用复合索引的多个字段时,较大的
key_len是有利的,因为它表明查询条件使用了索引的多个部分,从而可能减少全表扫描的需求。 - 索引的效率:另一方面,较小的
key_len可能意味着查询条件已经足够过滤掉大多数不匹配的行,从而更快地找到所需的记录。
实际应用中的考量
- 复合索引:如果你的查询经常使用复合索引的前几个字段,而不使用全部字段,那么你可能希望
key_len较小,这样查询效率可能更高,因为数据库引擎不需要扫描索引的所有部分。 - 单字段索引:如果你有一个单字段索引,那么
key_len的大小主要取决于这个字段的类型。对于简单的查询,key_len较小可能是好事。
总结来说,key_len 并不是越大或越小越好,而是要根据查询的具体情况来衡量。当 key_len 充分利用了索引的关键字段,并且有效过滤数据时,这通常是一个高效的查询设计。
set names utf8mb4; set foreign_key_checks = 0; drop table if exists `user`; create table `user` ( `id` bigint not null auto_increment, `name` varchar(10) character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci null default null, `age` int null default null, `sex` char(1) character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci null default null, `create_time` datetime null default null, primary key (`id`) using btree, index `idx_name`(`name` asc) using btree, index `idx_age`(`age` asc) using btree, index `idx_sex`(`sex` asc) using btree ) engine = innodb auto_increment = 3 character set = utf8 collate = utf8_general_ci row_format = dynamic; insert into `user` values (1, 'tom', 18, '男', '2024-08-17 10:09:00'); insert into `user` values (2, 'zimu', 18, '男', '2024-08-07 10:09:30');
- 使用explain 进行测试
| 列类型 | 是否为空 | 长度 | key_len | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tinyint | 允许null | 1 | key_len = 1 + 1 | 允许null,key_len长度加1 |
| tinyint not null | 不允许null | 1 | key_len = 1 | 不允许null |
| int | 允许null | 4 | key_len = 4 + 1 | 允许null,key_len长度加1 |
| int not null | 不允许null | 4 | key_len = 4 | 不允许null |
| bigint | 允许null | 8 | key_len = 8 + 1 | 允许null,key_len长度加1 |
| bigint not null | 不允许null | 8 | key_len = 8 | 不允许null |
| char(1) | 允许null | utf8mb4=4, utf8=3, gbk=2 | key_len = 1*3 + 1 | 允许null,字符集utf8,key_len长度加1 |
| char(1) not null | 不允许null | utf8mb4=4, utf8=3, gbk=2 | key_len = 1*3 | 不允许null,字符集utf8 |
| varchar(10) | 允许null | utf8mb4=4, utf8=3, gbk=2 | key_len = 10*3 + 2 + 1 | 动态列类型,key_len长度加2,允许null,key_len长度加1 |
| varchar(10) not null | 不允许null | utf8mb4=4, utf8=3, gbk=2 | key_len = 10*3 + 2 | 动态列类型,key_len长度加2 |
- id字段类型为bigint,长度为8,id为主键,不允许null ,key_len = 8 。
explain select * from user where id = 1;

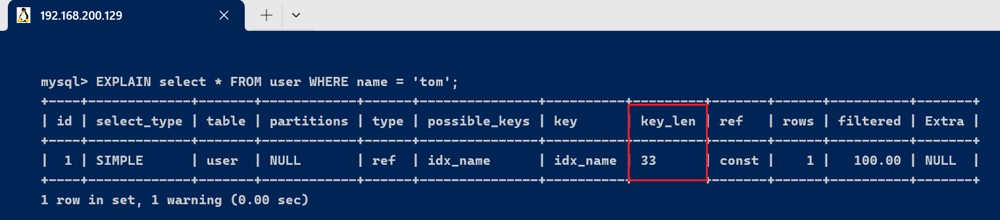
- name的字段类型是varchar(10),允许null,字符编码是utf8,一个字符占用3个字节,varchar为动态类型,key长度加2,key_len = 10 * 3 + 2 + 1 = 33 。
explain select * from user where name = 'tom';
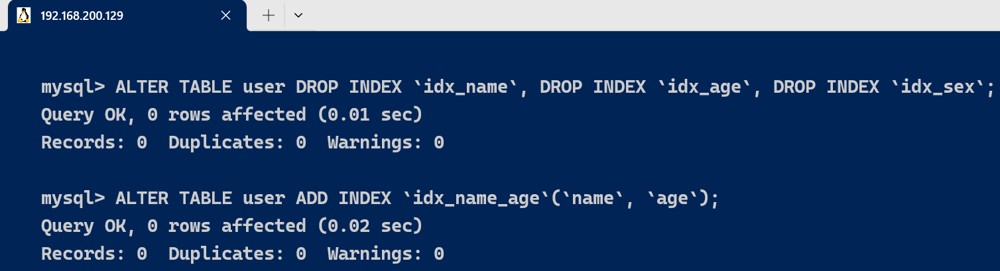
联合索引key_len计算
我们删除user表其他辅助索引,建立一个联合索引
alter table user drop index `idx_name`, drop index `idx_age`, drop index `idx_sex`;
alter table user add index `idx_name_age`(`name`, `age`);
1、部分索引生效的情况
我们使用name进行查询
explain select * from user where name = 'tom';
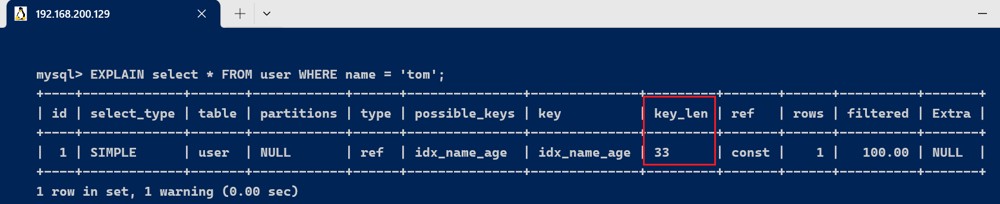
由于联合索引,根据最左匹配原则,使用到索引只有name这一列,name的字段类型是varchar(10),允许null,字符编码是utf8,一个字符占用3个字节,varchar为动态类型,key长度加2,key_len = 10 * 3+2 + 1 = 33 。
2、联合索引完全使用索引的情况
explain select * from user where name = '张三' and age = 19;
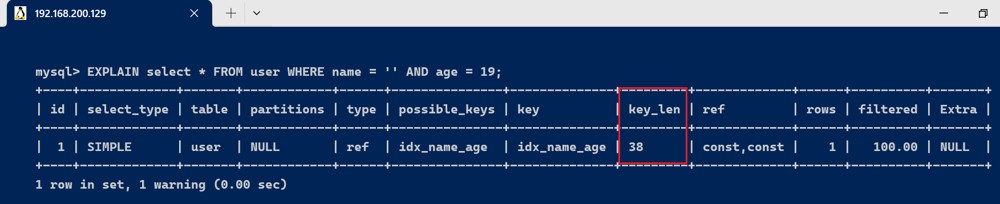
由于联合索引,使用到(name,age)联合索引,name的字段类型是varchar(10),允许null,字符编码是utf8,一个字符占用3个字节,varchar为动态类型,key长度加2,key_len = 10 * 3 + 2 + 1 = 33 ,age的字段类型是int,长度为4,允许null ,key_len = 4 + 1 = 5 。联合索引的key_len 为 key_len = 33+5 = 38。
3.7、ref 字段
显示索引的哪一列被使用了,如果可能的话,是一个常数。哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列上的值
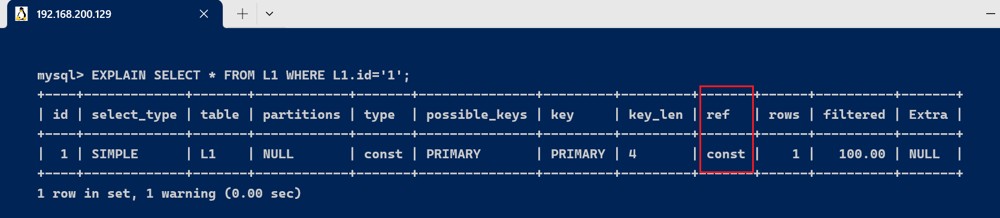
- l1.id=‘1’; 1是常量 , ref = const
explain select * from l1 where l1.id='1';
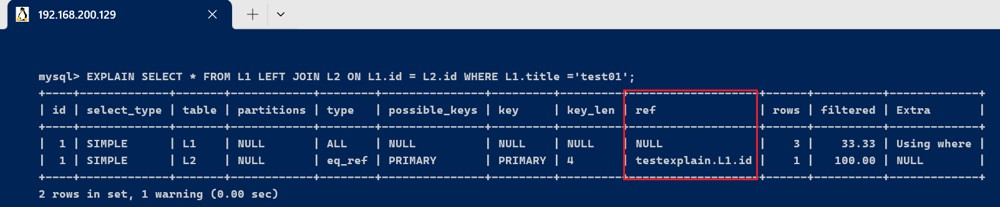
- l2表被关联查询的时候,使用了主键索引, 而值使用的是驱动表(执行计划中靠前的表是驱动表)l1表的id, 所以 ref = test_explain.l1.id
explain select * from l1 left join l2 on l1.id = l2.id where l1.title ='test01';
什么是驱动表 ?
- 多表关联查询时,第一个被处理的表就是驱动表,使用驱动表去关联其他表.
- 驱动表的确定非常的关键,会直接影响多表关联的顺序,也决定后续关联查询的性能
驱动表的选择要遵循一个规则:
在对最终的结果集没有影响的前提下,优先选择结果集最小的那张表作为驱动表
3.8、rows 字段
表示mysql根据表统计信息及索引选用情况,估算的找到所需的记录所需要读取的行数;越少越好
- 使用like 查询,会产生全表扫描, l2中有3条记录,就需要读取3条记录进行查找
explain select * from l1,l2 where l1.id = l2.id and l2.title like '%tes%';
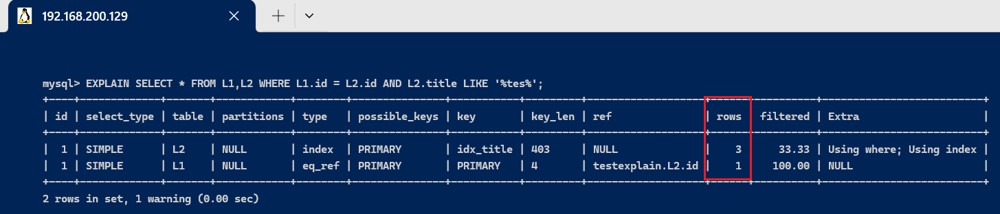
- 如果使用等值查询, 则可以直接找到要查询的记录,返回即可,所以只需要读取一条
explain select * from l1,l2 where l1.id = l2.id and l2.title = 'test03';
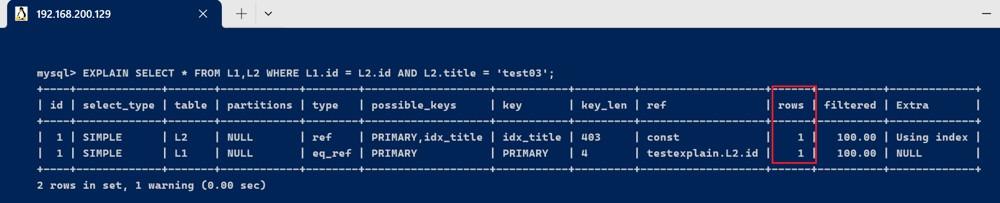
总结: 当我们需要优化一个sql语句的时候,我们需要知道该sql的执行计划,比如是全表扫描,还是索引扫描; 使用explain 关键字可以模拟优化器执行sql 语句,从而知道mysql 是如何处理sql 语句的,方便我们开发人员有针对性的对sql进行优化.
- 表的读取顺序。(对应id)
- 数据读取操作的操作类型。(对应select_type)
- 哪些索引可以使用。(对应possible_keys)
- 哪些索引被实际使用。(对应key)
- 每张表有多少行被优化器查询。(对应rows)
- 评估sql的质量与效率 (对应type)
3.9、filtered 字段
它指返回结果的行占需要读到的行(rows列的值)的百分比
3.9、extra 字段
extra 是 explain 输出中另外一个很重要的列,该列显示mysql在查询过程中的一些详细信息
create table users ( uid int primary key auto_increment, uname varchar(20), age int(11) ); insert into users values(null, 'lisa',10); insert into users values(null, 'lisa',10); insert into users values(null, 'rose',11); insert into users values(null, 'jack', 12); insert into users values(null, 'sam', 13);
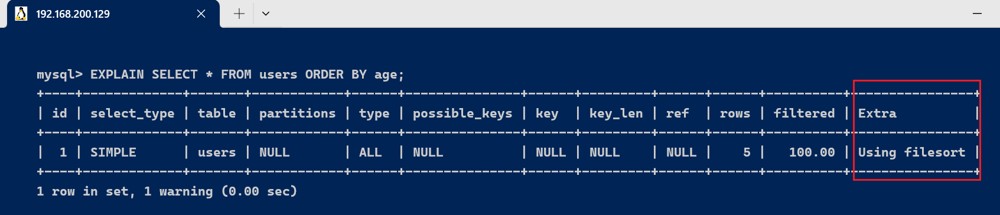
- using filesort
explain select * from users order by age;
执行结果extra为using filesort ,这说明,得到所需结果集,需要对所有记录进行文件排序。这类sql语句性能极差,需要进行优化。
典型的,在一个没有建立索引的列上进行了order by,就会触发filesort,常见的优化方案是,在order by的列上添加索引,避免每次查询都全量排序。
filtered 它指返回结果的行占需要读到的行(rows列的值)的百分比
- using temporary
explain select count(*),uname from users where uid > 2 group by uname;
执行结果extra为using temporary ,这说明需要建立临时表 (temporary table) 来暂存中间结果。性能消耗大, 需要创建一张临时表, 常见于group by语句中. 需配合sql执行过程来解释, 如果group by和where索引条件不同, 那么group by中的字段需要创建临时表分组后再回到原查询表中.如果查询条件where和group by是相同索引字段, 那么就不需要临时表.
- using where
explain select * from users where age=10;
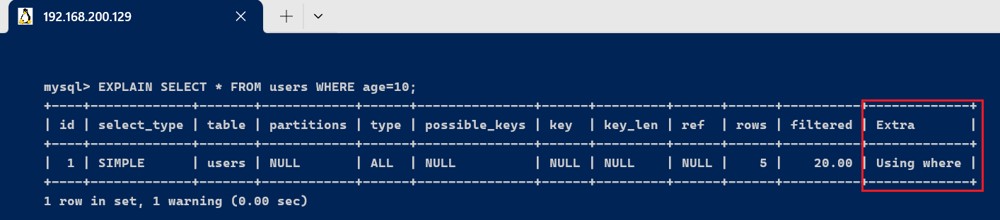
此语句的执行结果extra为using where,表示使用了where条件过滤数据。需要注意的是:
- 返回所有记录的sql,不使用where条件过滤数据,大概率不符合预期,对于这类sql往往需要进行优化;
- 使用了where条件的sql,并不代表不需要优化,往往需要配合explain结果中的type(连接类型)来综合判断。例如本例查询的 age 未设置索引,所以返回的type为all,仍有优化空间,可以建立索引优化查询。
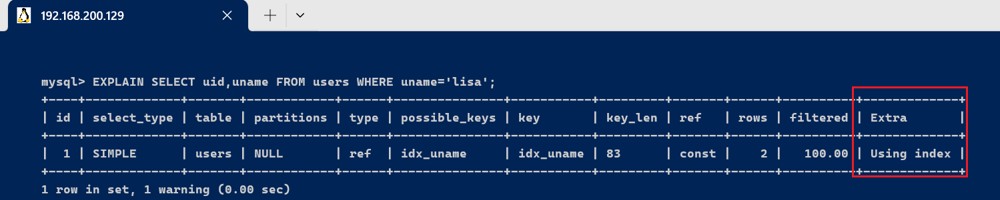
- using index
表示直接访问索引就能够获取到所需要的数据(覆盖索引) , 不需要通过索引回表.
-- 为uname创建索引 alter table users add index idx_uname(uname);
explain select uid,uname from users where uname='lisa';

此句执行结果为extra为using index,说明sql所需要返回的所有列数据均在一棵索引树上,而无需访问实际的行记录。
using join buffer (block nested loop):
- 这个
extra字段的值表明 mysql 在执行嵌套循环连接时使用了连接缓冲区。这通常发生在没有可用的合适索引时,mysql 会将一个表的数据加载到内存中的缓冲区,然后逐一扫描另一个表,以找到满足连接条件的行。 - block nested loop 是指 mysql 会将外部表(在本例中是
u1)的部分数据块加载到缓冲区,然后与内部表(在本例中是子查询派生表u2)进行匹配。这样可以减少对磁盘的访问次数,提高查询效率。
需要进行嵌套循环计算.
alter table users add column sex char(1);
update users set sex = '0' where uname in ('lisa', 'rose');
update users set sex = '1' where uname in ('jack', 'sam');
explain select *
from users u1
left join
(select * from users where sex = '0') u2
on u1.uname = u2.uname;
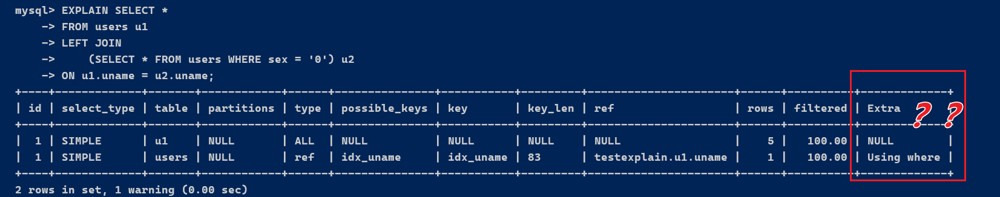
没有显示 using join buffer,可能是因为查询优化器在这个具体的场景下能够有效地使用索引,因此不需要使用连接缓冲区。在这种情况下,mysql 直接使用了 ref 类型的连接(通过索引进行连接),而不是需要缓冲区的嵌套循环连接。
可以删除或修改表上的索引,以便让 mysql 在执行查询时无法使用现有的索引,从而被迫使用连接缓冲区。
alter table users drop index idx_uname;
explain select *
from users u1
left join
(select * from users where sex = '0') u2
on u1.uname = u2.uname;
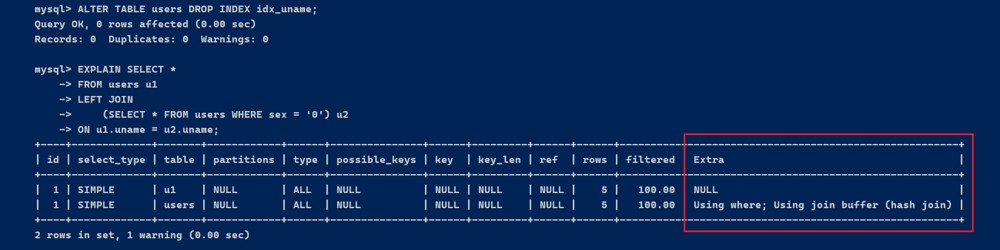
执行结果extra为using join buffer (block nested loop) 说明,需要进行嵌套循环计算, 这里每个表都有五条记录,内外表查询的type都为all。
问题在于 两个关联表join 使用 uname,关联字段均未建立索引,就会出现这种情况。
常见的优化方案是,在关联字段上添加索引,避免每次嵌套循环计算。
- using index condition
搜索条件中虽然出现了索引列,但是有部分条件无法使用索引,会根据能用索引的条件先搜索一遍再匹配无法使用索引的条件。
using index condition 叫作 index condition pushdown optimization (索引下推优化)。index condition pushdown (icp)是mysql使用索引从表中检索行的一种优化。如果没有icp,存储引擎将遍历索引以定位表中的行,并将它们返回给mysql服务器,服务器将判断行的where条件。在启用icp的情况下,如果可以只使用索引中的列来计算where条件的一部分,mysql服务器就会将where条件的这一部分推到存储引擎中。然后,存储引擎通过使用索引条目来评估推入的索引条件,只有当满足该条件时,才从表中读取行。icp可以减少存储引擎必须访问基表的次数和mysql服务器必须访问存储引擎的次数。
create table employees (
id int primary key auto_increment,
first_name varchar(50),
last_name varchar(50),
age int,
department_id int,
salary decimal(10, 2),
hire_date date
);
insert into employees (first_name, last_name, age, department_id, salary, hire_date) values
('john', 'doe', 30, 1, 60000.00, '2015-03-01'),
('jane', 'doe', 28, 2, 65000.00, '2016-07-15'),
('mike', 'smith', 45, 3, 75000.00, '2010-10-22'),
('sara', 'jones', 32, 1, 55000.00, '2018-01-12'),
('tom', 'brown', 29, 2, 58000.00, '2017-05-18');
接着,我们在 last_name 和 age 字段上创建复合索引:
create index idx_lastname_age on employees(last_name, age);
编写一个查询,包含部分能利用索引的条件和部分不能利用索引的条件:
explain select * from employees where last_name = 'doe' and age > 25 and salary > 60000;
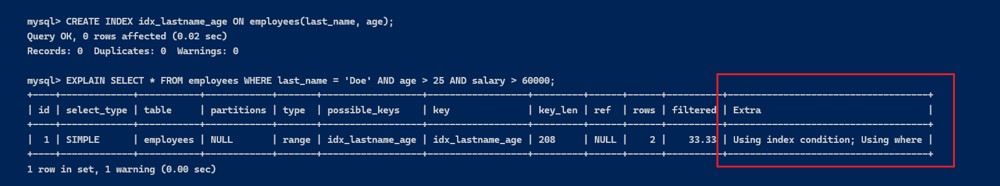
这一行表明 mysql 在查询中使用了 index condition pushdown 优化。
在这个例子中,last_name = 'doe' 和 age > 25 可以利用复合索引 idx_lastname_age,因此 mysql 使用索引条件下推技术,在存储引擎层面尽量减少访问行数据的次数。
salary > 60000 是不能利用索引的条件,但由于使用了 icp,存储引擎会先根据 last_name 和 age 进行初步过滤,然后再把符合条件的行返回给 mysql 服务器,服务器进一步应用 salary > 60000 的过滤。
总结:
index condition pushdown (icp) 是一种优化技术,允许 mysql 在存储引擎层面应用部分 where 条件,从而减少需要从表中读取的行数。这可以提高查询性能,尤其是在涉及复合索引时。
using index condition 提示表示 mysql 已经应用了 icp 优化。通过使用复合索引和带有多条件的查询,可以显式地观察到这个优化技术的作用。
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=mzkwotcznzuxmq==&mid=2247484180&idx=1&sn=2cfeba47a57b0d27d297de2037928080&chksm=c137685cf640e14abf7215d3a063e199b1d9aabf5e659b5113230bfea3a5a79ec84479545682#rd
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。
您想发表意见!!点此发布评论





发表评论