Mysql创建表以及数据库crud语句举例详细讲解
30人参与 • 2025-08-18 • Mysql
一. 创建数据表
1.下面我们直接演示数据表的创建语句:
- field:指定列名
- datatype:指定列名的数据类型
- character set:若不指定字符集,就与所在数据库的字符集保持一致
- collate:校队规则,若不指定,就与所在数据库的字符集保持一致
-- 演示表的创建 create table lrx_t1( field1 datatype, field2 datatype, field3 datatype )character set 字符集 collate 校队规则 engine 存储引擎;
2.删除数据表
drop table lrx_t1;
3.下面我们做一个练习
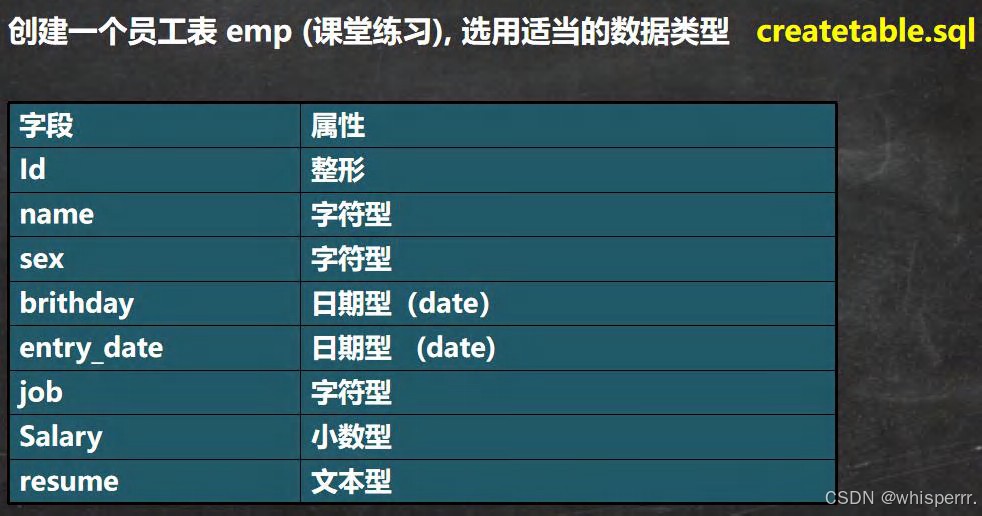
#创建表的课堂练习 -- 字段属性 -- id 整形 -- name 字符型 -- sex 字符型 -- brithday 日期型(date) -- entry_date 日期型 (date) -- job 字符型 -- salary 小数型 -- resume 文本型 -- 自己一定要练习一把 create table `emp` ( id int, `name` varchar(32), sex char(1), brithday date, entry_date datetime, job varchar(32), salary double, `resume` text) charset utf8 collate utf8_bin engine innodb; -- 添加一条 insert into `emp` values(100, '小妖怪', '男', '2000-11-11', '2010-11-10 11:11:11', '巡山的', 3000, '大王叫我来巡山'); -- 查询 select * from `emp`;
二. 修改表结构
这是对表的结构进行修改,比如添加列,删除列,修改表的名字,字符集,引擎等
- 添加列
alter table lrx_t1 add `name` varchar(32) not null default '';
- 删除列
alter table lrx_t1 drop `name`;
- 修改表的名字
rname table lrx_t1 to liu;
- 修改列,比如修改名字的长度为60,注意,我们已经改了表名
altre table liu modify `name` varchar(60)
- 列名·name`改为 my_name
alter table liu change `name` my_name varchar(32) not null default ' ';
- 修改表的字符集为utf8
alter table liu character set utf8;
- 显示表的结构
desc liu;
三. 数据库crud语句
3.1insert语句(添加数据)
1.基本语句
insert into table_name values (vaulue...);
2.使用细节
- 插入的数据应与字段的数据类型相同。
比如 把 ‘abc’ 添加到 int 类型会错误
insert intogoods(id, goods_name, price)
values(‘雷军’, ‘小米手机’, 2000);- 数据的长度应在列的规定范围内,例如:不能将一个长度为 80 的字符串加入到长度为 40 的列中。
insert intogoods(id, goods_name, price)
values(40, ‘vovo 手机 vovo 手机 vovo 手机 vovo 手机 vovo 手机’, 3000);- 在 values 中列出的数据位置必须与被加入的列的排列位置相对应。
insert intogoods(id, goods_name, price) – 不对
values(‘vovo 手机’,40, 2000); –- 字符和日期型数据应包含在单引号中。
insert intogoods(id, goods_name, price)
values(40, vovo 手机, 3000); – 错误的 vovo 手机 应该 ‘vovo 手机’- 列可以插入空值[前提是该字段允许为空],insert into table value(null)
insert intogoods(id, goods_name, price)
values(40, ‘vovo 手机’, null);- insert into tab_name (列名…) values (),(),() 形式添加多条记录
insert intogoods(id, goods_name, price)
values(50, ‘三星手机’, 2300),(60, ‘海尔手机’, 1800);- 如果是给表中的所有字段添加数据,可以不写前面的字段名称
insert intogoodsvalues(70, ‘ibm 手机’, 5000);- 默认值的使用,当不给某个字段值时,如果有默认值就会添加默认值,否则报错,如果某个列 没有指定 not null ,那么当添加数据时,没有给定值,则会默认给 null , 如果我们希望指定某个列的默认值,可以在创建表时指定
insert intogoods(id, goods_name)
values(80, ‘格力手机’);
select * from goods;
insert intogoods2(id, goods_name)
values(10, ‘小米手机’);
select * from goods2;
3.2update语句(更新数据)
1.使用update语句来修改表中的数据

2.基本使用,我们先看一个题目

-- 演示 update 语句
-- 要求: 在上面创建的 employee 表中修改表中的纪录
-- 1. 将所有员工薪水修改为 5000 元。[如果没有带 where 条件,会修改所有的记录,因此要小心]
update employee set salary = 5000
-- 2. 将姓名为 小妖怪 的员工薪水修改为 3000 元。
update employee
set salary = 3000
where user_name = '小妖怪'
-- 3. 将 老妖怪 的薪水在原有基础上增加 1000 元
insert into employee
values(200, '老妖怪', '1990-11-11', '2000-11-11 10:10:10', '捶背的', 5000, '给大王捶背', 'd:\\a.jpg');
update employee
set salary = salary + 1000
where user_name = '老妖怪' -- 可以修改多个列的值
update employee
set salary = salary + 1000 , job = '出主意的'
where user_name = '老妖怪'
3.updata使用的四个细节
- 1.update语法可以用新值更新原有表行中的各列。
- 2.set子句指示要修改哪些列和要给予哪些值。
- 3.where子句指定应更新哪些行。如没有where子句,则更新所有的行(记录),因此老师提醒一定小心。
- 4.如果需要修改多个字段,可以通过set字段1=值1,字段2=值2…
3.3delect语句(删除数据)
1.使用delect语句删除表中数据
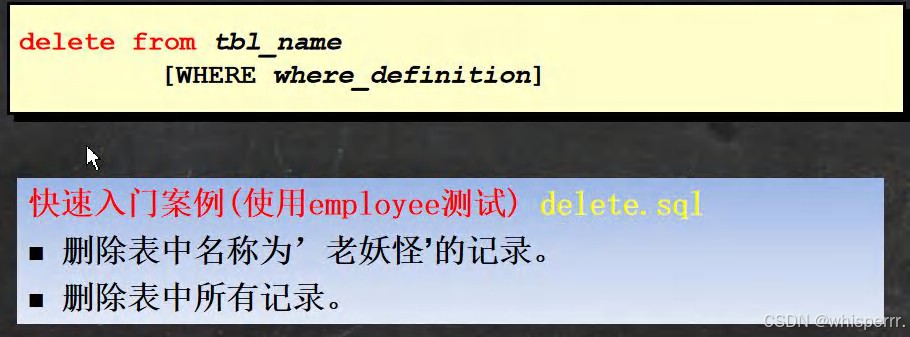
2.快速入门案例解答
-- 删除表中名称为'老妖怪'的记录。 delete from employee where user_name = '老妖怪'; -- 删除表中所有记录, 老师提醒,一定要小心 delete from employee; -- delete 语句不能删除某一列的值(可使用 update 设为 null 或者 '') update employee set job = '' where user_name = '老妖怪'; -- 要删除这个表 drop table employee;
3.delect使用细节
- 如果不使用where子句,将删除表中所有数据。
- delete语句不能删除某一列的值(可使用update设为null或者")
- 使用delete语句仅删除记录,不删除表本身。如要删除表,使用drop table 表名;
3.4select语句(查找数据)
查询语句我们这里简单讲述一下单表查询
3.4.1单表查询
1.基本语法

- 1.select指定查询哪些列的数据。
- 2.column指定列名。
- 3.*号代表查询所有列。
- 4 from指定查询哪张表。
- 5.distinct可选,指显示结果时,是否去掉重复数据
2,下面我们演示一下案例,在演示之前,我们先创建一个表
create table student( id int not null default 1, name varchar(20) not null default '', chinese float not null default 0.0, english float not null default 0.0, math float not null default 0.0 ); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(1,'韩顺平',89,78,90); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(2,'张飞',67,98,56); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(3,'宋江',87,78,77); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(4,'关羽',88,98,90); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(5,'赵云',82,84,67); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(6,'欧阳锋',55,85,45); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(7,'黄蓉',75,65,30); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(8,'韩信',45,65,99); select * from student;
表创建之后,我们看一下题目要求

-- 查询表中所有学生的信息。 select * from student; -- 查询表中所有学生的姓名和对应的英语成绩。 select `name`,english from student; -- 过滤表中重复数据 distinct 。 select distinct english from student; -- 要查询的记录,每个字段都相同,才会去重 select distinct `name`, english from student;
3.使用表达式对查询的列进行运算

4.在 select 语句中可使用 as 语句

5.在 where 子句中经常使用的运算符
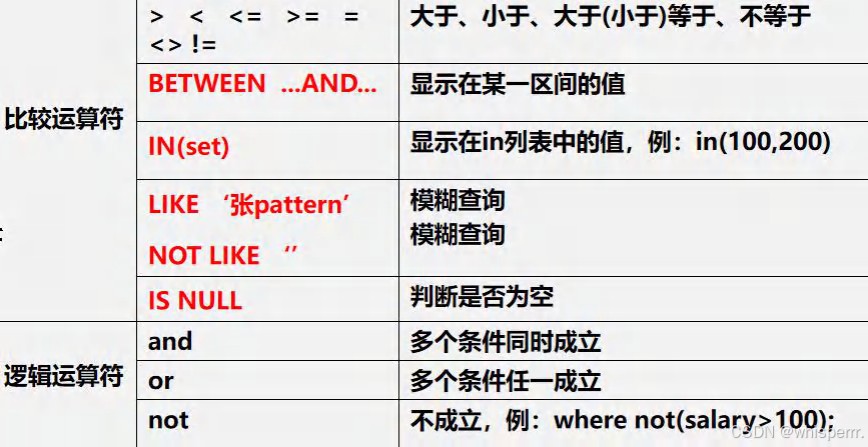
下面我们继续根据上面创建的表来练习题目

-- select 语句 -- 查询姓名为赵云的学生成绩 select * from student where `name` = '赵云' -- 查询英语成绩大于 90 分的同学 select * from student where english > 90 -- 查询总分大于 200 分的所有同学 select * from student where (chinese + english + math) > 200
6.使用 order by 子句排序查询结果
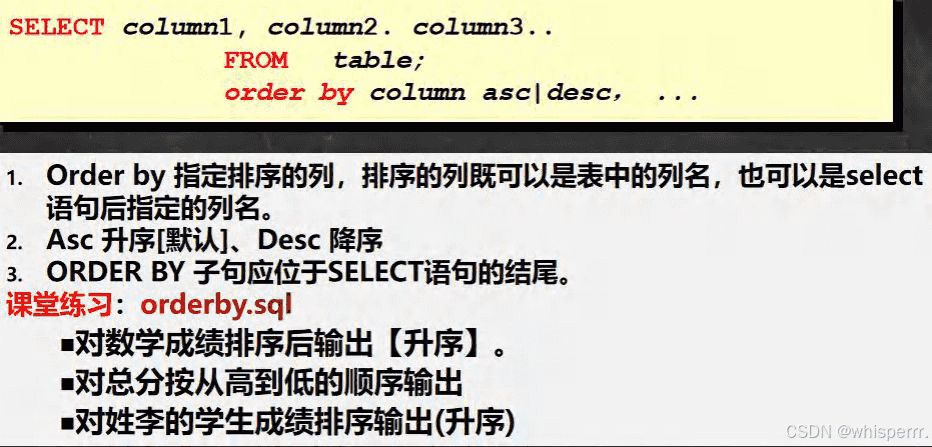
-- 演示 order by 使用 -- 对数学成绩排序后输出【升序】。 select * from student order by math; -- 对总分按从高到低的顺序输出 [降序] -- 使用别名排序 select `name` , (chinese + english + math) as total_score from student order by total_score desc; -- 对姓韩的学生成绩[总分]排序输出(升序) where + order by select `name`, (chinese + english + math) as total_score from student where `name` like '韩%' order by total_score;
总结
到此这篇关于mysql创建表以及数据库crud语句的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql创建表及crud语句内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!
赞 (0)
您想发表意见!!点此发布评论






发表评论