浅谈进程隐藏技术
383人参与 • 2024-08-04 • 企业安全
前言
在之前几篇文章已经学习了解了几种钩取的方法
● 浅谈调试模式钩取
● 浅谈热补丁
● 浅谈内联钩取原理与实现
● 导入地址表钩取技术
这篇文章就利用钩取方式完成进程隐藏的效果。
进程遍历方法
在实现进程隐藏时,首先需要明确遍历进程的方法。
createtoolhelp32snapshot
createtoolhelp32snapshot函数用于创建进程的镜像,当第二个参数为0时则是创建所有进程的镜像,那么就可以达到遍历所有进程的效果。
#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> #include <tlhelp32.h> int main() { //设置编码,便于后面能够输出中文 setlocale(lc_all, "zh_cn.utf-8"); //创建进程镜像,参数0代表创建所有进程的镜像 handle hsnapshot = createtoolhelp32snapshot(th32cs_snapprocess, 0); if (hsnapshot == invalid_handle_value) { std::cout << "create error" << std::endl; exit(-1); } /* * typedef struct tagprocessentry32 { * dword dwsize; 进程信息结构体大小,首次调用之前必须初始化 * dword cntusage; 引用进程的次数,引用次数为0时,则进程结束 * dword th32processid; 进程的id * ulong_ptr th32defaultheapid; 进程默认堆的标识符,除工具使用对我们没用 * dword th32moduleid; 进程模块的标识符 * dword cntthreads; 进程启动的执行线程数 * dword th32parentprocessid; 父进程id * long pcpriclassbase; 进程线程的基本优先级 * dword dwflags; 保留 * tchar szexefile[max_path]; 进程的路径 * } processentry32; * typedef processentry32 *pprocessentry32; */ processentry32 pi; pi.dwsize = sizeof(processentry32); //取出第一个进程 bool bret = process32first(hsnapshot, &pi); while (bret) { wprintf(l"进程路径:%s\t进程号:%d\n", pi.szexefile, pi.th32processid); //取出下一个进程 bret = process32next(hsnapshot, &pi); } }
enumprocesses
enumprocesses用于将所有进程号的收集。
#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> #include <psapi.h> int main() { setlocale(lc_all, "zh_cn.utf-8"); dword processes[1024], dwresult, size; unsigned int i; //收集所有进程的进程号 if (!enumprocesses(processes, sizeof(processes), &dwresult)) { std::cout << "enum error" << std::endl; } //进程数量 size = dwresult / sizeof(dword); for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { //判断进程号是否为0 if (processes[i] != 0) { //用于存储进程路径 tchar szprocessname[max_path] = { 0 }; //使用查询权限打开进程 handle hprocess = openprocess(process_query_information | process_vm_read, false, processes[i]); if (hprocess != null) { hmodule hmod; dword dwneeded; //收集该进程的所有模块句柄,第一个句柄则为文件路径 if (enumprocessmodules(hprocess, &hmod, sizeof(hmod), &dwneeded)) { //根据句柄获取文件路径 getmodulebasename(hprocess, hmod, szprocessname, sizeof(szprocessname) / sizeof(tchar)); } wprintf(l"进程路径:%s\t进程号:%d\n", szprocessname, processes[i]); } } } }
zwquerysysteminfomation
zwquerysysteminfomation函数是createtoolhelp32snapshot函数与enumprocesses函数底层调用的函数,也用于遍历进程信息。代码参考https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1454933
#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> #include <ntstatus.h> #include <winternl.h> #pragma comment(lib, "ntdll.lib") //定义函数指针 typedef ntstatus(winapi* ntquerysysteminformation)( in system_information_class systeminformationclass, in out pvoid systeminformation, in ulong systeminformationlength, out pulong returnlength ); int main() { //设置编码 setlocale(lc_all, "zh_cn.utf-8"); //获取模块地址 hinstance ntdll_dll = getmodulehandle(l"ntdll.dll"); if (ntdll_dll == null) { std::cout << "get module error" << std::endl; exit(-1); } ntquerysysteminformation zwquerysysteminformation = null; //获取函数地址 zwquerysysteminformation = (ntquerysysteminformation)getprocaddress(ntdll_dll, "zwquerysysteminformation"); if (zwquerysysteminformation != null) { system_basic_information sbi = { 0 }; //查询系统基本信息 ntstatus status = zwquerysysteminformation(systembasicinformation, (pvoid)&sbi, sizeof(sbi), null); if (status == status_success) { wprintf(l"处理器个数:%d\r\n", sbi.numberofprocessors); } else { wprintf(l"zwquerysysteminfomation error\n"); } dword dwneedsize = 0; byte* pbuffer = null; wprintf(l"\t----所有进程信息----\t\n"); psystem_process_information psp = null; //查询进程数量 status = zwquerysysteminformation(systemprocessinformation, null, 0, &dwneedsize); if (status == status_info_length_mismatch) { pbuffer = new byte[dwneedsize]; //查询进程信息 status = zwquerysysteminformation(systemprocessinformation, (pvoid)pbuffer, dwneedsize, null); if (status == status_success) { psp = (psystem_process_information)pbuffer; wprintf(l"\tpid\t线程数\t工作集大小\t进程名\n"); do { //获取进程号 wprintf(l"\t%d", psp->uniqueprocessid); //获取线程数量 wprintf(l"\t%d", psp->numberofthreads); //获取工作集大小 wprintf(l"\t%d", psp->workingsetsize / 1024); //获取路径 wprintf(l"\t%s\n", psp->imagename.buffer); //移动 psp = (psystem_process_information)((pbyte)psp + psp->nextentryoffset); } while (psp->nextentryoffset != 0); delete[]pbuffer; pbuffer = null; } else if (status == status_unsuccessful) { wprintf(l"\n status_unsuccessful"); } else if (status == status_not_implemented) { wprintf(l"\n status_not_implemented"); } else if (status == status_invalid_info_class) { wprintf(l"\n status_invalid_info_class"); } else if (status == status_info_length_mismatch) { wprintf(l"\n status_info_length_mismatch"); } } } }
进程隐藏
通过上述分析可以知道遍历进程的方式有三种,分别是利用createtoolhelp32snapshot、enumprocesses以及zwquerysysteminfomation函数
但是createtoolhelp32snapshot与enumprocesses函数底层都是调用了zwquerysysteminfomation函数,因此我们只需要钩取该函数即可。
由于测试环境是win11,因此需要判断在win11情况下底层是否还是调用了zwquerysysteminfomation函数。
可以看到在win11下还是会调用zwquerysysteminfomation函数,在用户态下该函数的名称为ntquerysysteminformation函数。
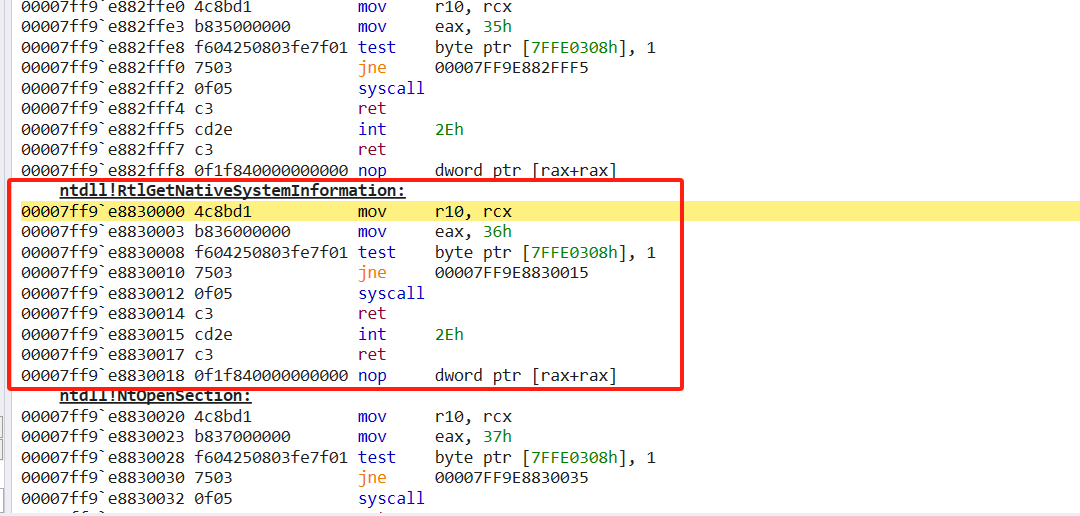
这里采用内联钩取的方式对zwquerysysteminfomation进行钩取处理,具体怎么钩取在浅谈内联钩取原理与实现已经介绍过了,这里就不详细说明了。这里对自定义的zwquerysysteminfomation函数进行说明。
首先第一步需要进行脱钩处理,因为后续需要用到初始的zwquerysysteminfomation函数,紧接着获取待钩取函数的地址即可。
... //脱钩 unhook("ntdll.dll", "zwquerysysteminformation", g_porgbytes); hmodule hmodule = getmodulehandlea("ntdll.dll"); //获取待钩取函数的地址 proc pfnold = getprocaddress(hmodule, "zwquerysysteminformation"); //调用原始的zwquerysysteminfomation函数 ntstatus status = ((ntquerysysteminformation)pfnold)(systeminformationclass, systeminformation, systeminformationlength, returnlength); ...
为了隐藏指定进程,我们需要遍历进程信息,找到目标进程并且删除该进程信息实现隐藏的效果。这里需要知道的是进程信息都存储在system_process_information结构体中,该结构体是通过单链表对进程信息进行链接。因此我们通过匹配进程名称找到对应的system_process_information结构体,然后进行删除即可,效果如下图。

通过单链表中删除节点的操作,取出目标进程的结构体。代码如下
... pcur = (psystem_process_information)(systeminformation); while (true) { if (!lstrcmpi(pcur->imagename.buffer, l"test.exe")) { //需要隐藏的进程是最后一个节点 if (pcur->nextentryoffset == 0) pprev->nextentryoffset = 0; //不是最后一个节点,则将该节点取出 else pprev->nextentryoffset += pcur->nextentryoffset; } //不是需要隐藏的节点,则继续遍历 else pprev = pcur; //链表遍历完毕 if (pcur->nextentryoffset == 0) break; pcur = (psystem_process_information)((pbyte)pcur + pcur->nextentryoffset); } ...
完整代码:https://github.com/h0pe-ay/hooktechnology/blob/main/processhidden/inlinehook.c
但是采用内联钩取的方法去钩取任务管理器就会出现一个问题,这里将断点取消,利用内联钩取的方式去隐藏进程。
首先利用bl命令查看断点

紧着利用 bc [id]删除断点

在注入之后任务管理器会在拷贝的时候发生异常
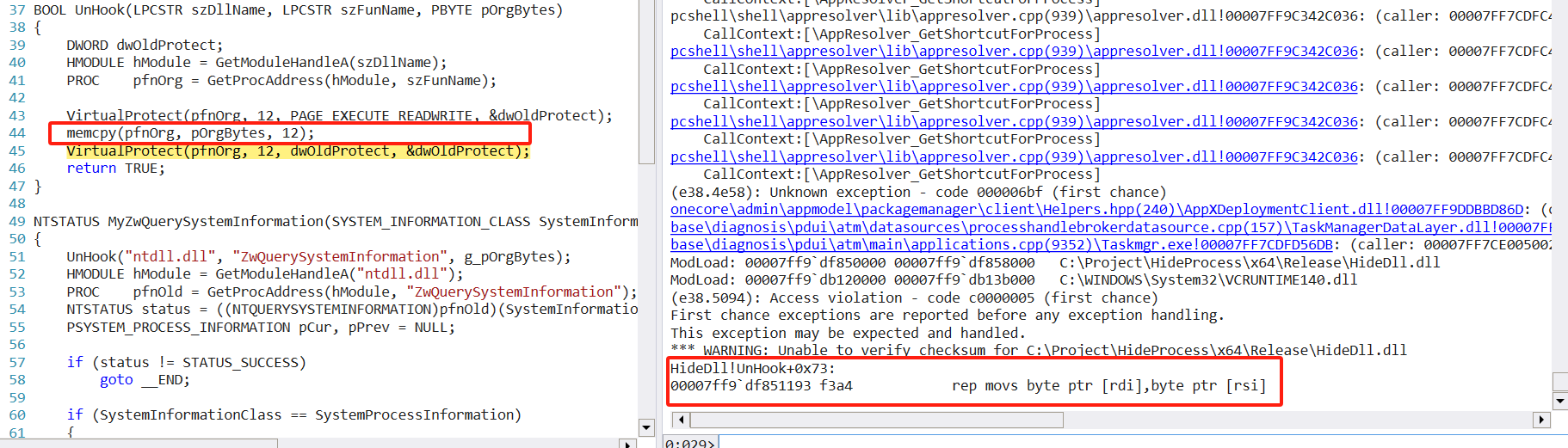
在经过一番调试后发现,由于多线程共同执行导致原本需要可写权限的段被修改为只读权限
在windbg可以用使用!vprot + address查看指定地址的权限,可以看到由于程序往只读权限的地址进行拷贝处理,所以导致了异常。

但是在执行拷贝阶段是先修改了该地址为可写权限,那么导致该原因的情况就是其他线程执行了权限恢复后切换到该线程中进行写,所以导致了这个问题。

因此内联钩取是存在多线程安全的问题,此时可以使用微软自己构建的钩取库detours,可以在钩取过程中确保线程安全。
【---- 帮助网安学习,以下所有学习资料免费领!领取资料加 we~@x:dctintin,备注 “开源中国” 获取!】
① 网安学习成长路径思维导图
② 60 + 网安经典常用工具包
③ 100+src 漏洞分析报告
④ 150 + 网安攻防实战技术电子书
⑤ 最权威 cissp 认证考试指南 + 题库
⑥ 超 1800 页 ctf 实战技巧手册
⑦ 最新网安大厂面试题合集(含答案)
⑧ app 客户端安全检测指南(安卓 + ios)
detours
项目地址:https://github.com/microsoft/detours
环境配置
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/linxmouse/p/14168712.html
使用vcpkg下载
vcpkg.exe install detours:x86-windows vcpkg.exe install detours:x64-windows vcpkg.exe integrate install
实例
挂钩
利用detours挂钩非常简单,只需要根据下列顺序,并且将自定义函数的地址与被挂钩的地址即可完成挂钩处理。
... //用于确保在 dll 注入或加载时,恢复被 detours 修改的进程镜像,保持稳定性 detourrestoreafterwith(); //开始一个新的事务来附加或分离 detourtransactionbegin(); //进行线程上下文的更新 detourupdatethread(getcurrentthread()); //挂钩 detourattach(&(pvoid&)truezwquerysysteminformation, zwquerysysteminformationex); //提交事务 error = detourtransactioncommit(); ...
脱钩
然后根据顺序完成脱钩即可。
... //开始一个新的事务来附加或分离 detourtransactionbegin(); //进行线程上下文的更新 detourupdatethread(getcurrentthread()); //脱钩 detourdetach(&(pvoid&)truezwquerysysteminformation, zwquerysysteminformationex); //提交事务 error = detourtransactioncommit(); ...
挂钩的原理
从上述可以看到,detours是通过事务确保了在dll加载与卸载时后的原子性,但是如何确保多线程安全呢?后续通过调试去发现。
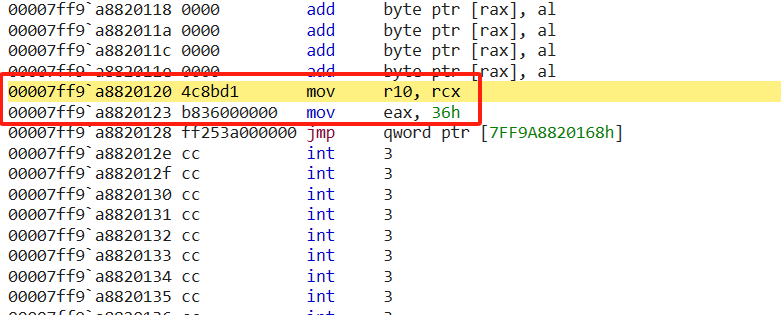
可以利用x ntdl!zwquerysysteminformation查看函数地址,可以看到函数的未被挂钩前的情况如下图。
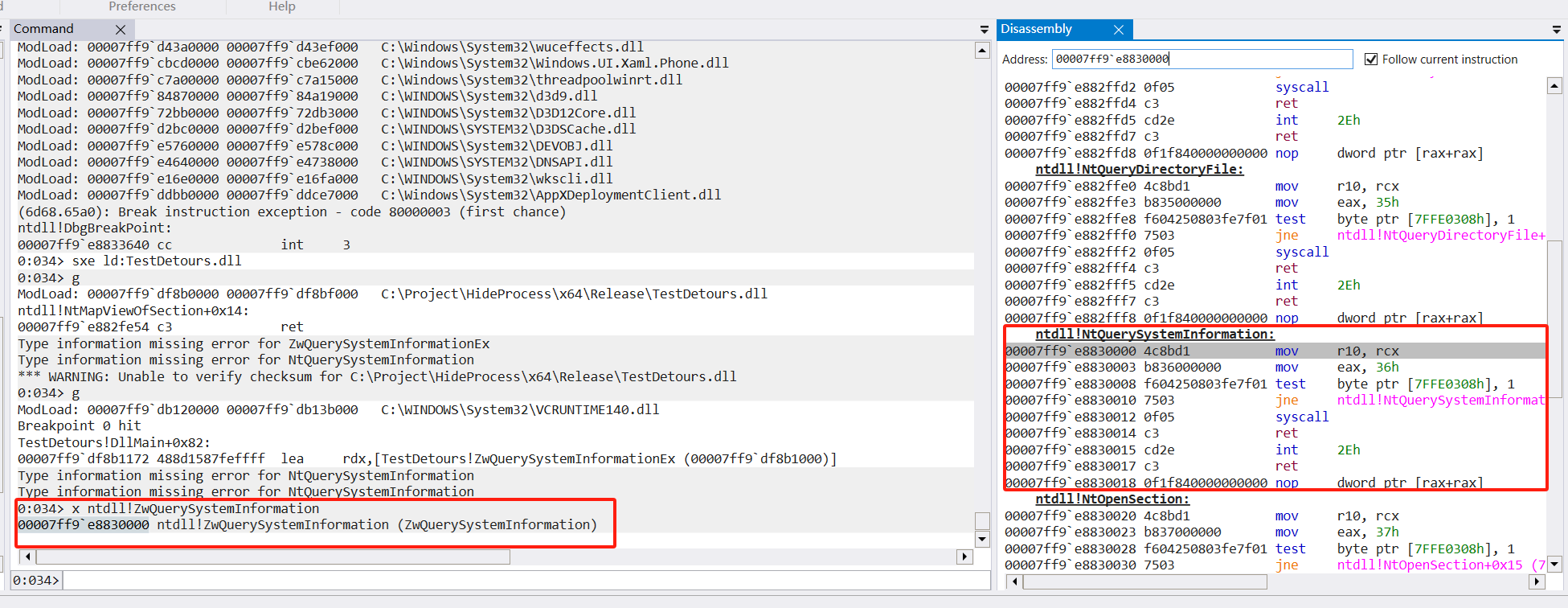
挂钩之后原始的指令被修改为一个跳转指令把前八个字节覆盖掉,剩余的3字节用垃圾指令填充。

该地址里面又是一个jmp指令,并且完成间接寻址的跳转。
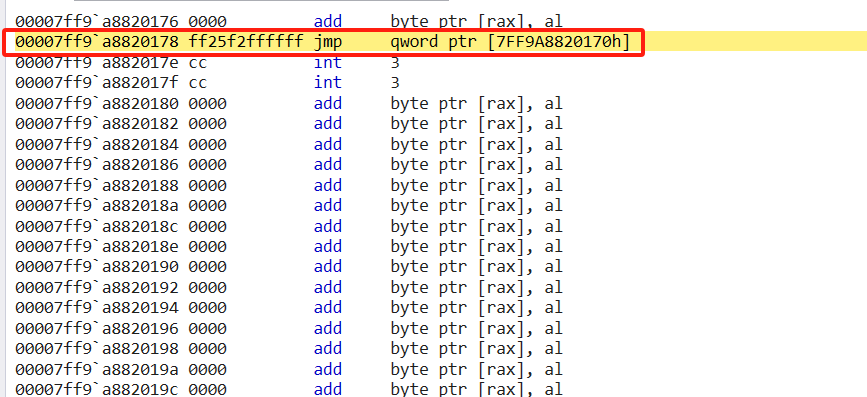
该地址是自定义函数zwquerysysteminformationex,因此该间接跳转是跳转到的自定义函数内部。
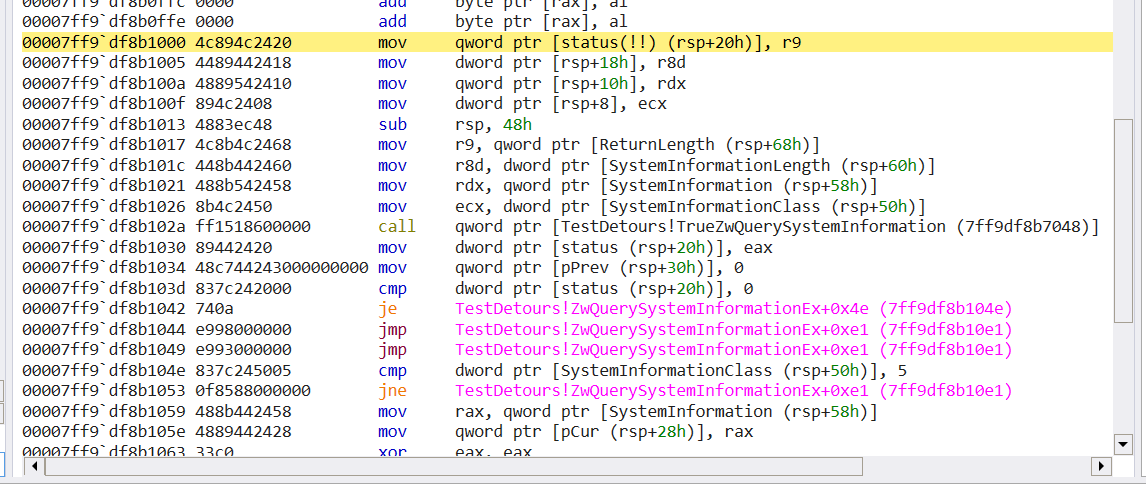
跳转到truezwquerysysteminformation内部发现zwquerysysteminformation函数内部的八字节指令被移动到该函数内部。紧接着又完成一个跳转。
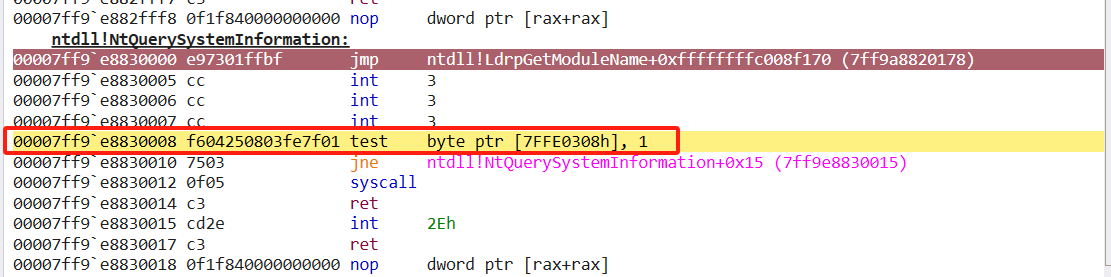
该跳转到zwquerysysteminformation函数内部紧接着完成zwquerysysteminformation函数的调用。
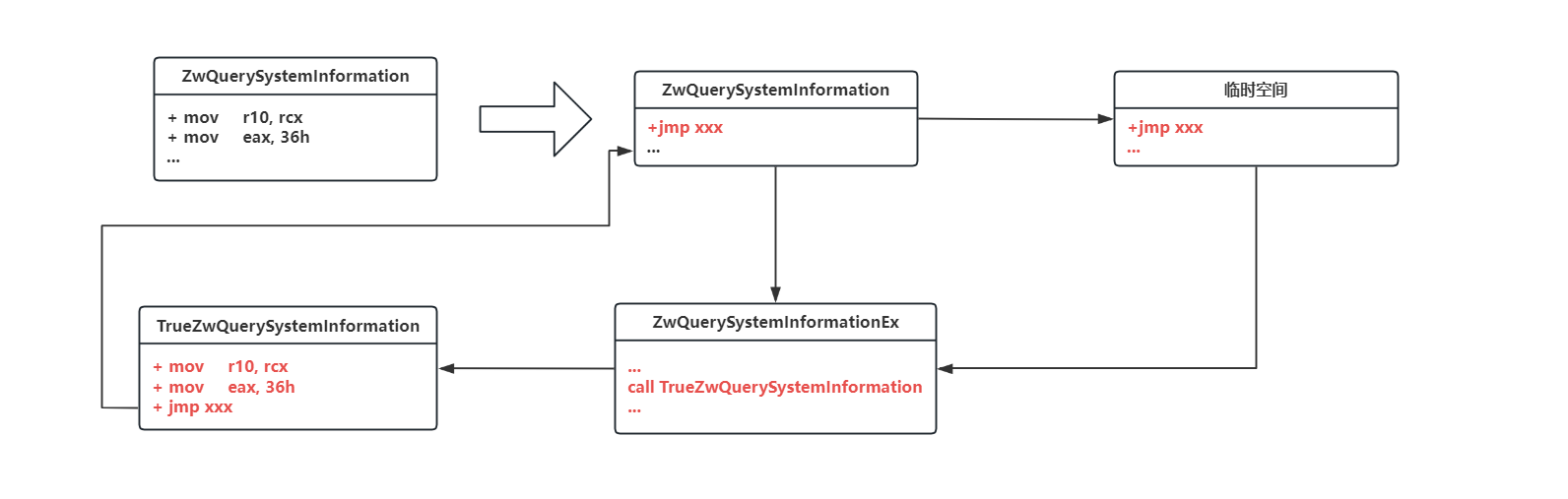
综上所述,整体流程如下图。实际上detours实际上使用的是热补丁的思路,但是detours并不是直接在原始的函数空间中进行补丁,而是开辟了一段临时空间,将指令存储在里面。因此在挂钩后不需要进行脱钩处理就可以调用原始函数。因此就不存在多线程中挂钩与脱钩的冲突。
完整代码:https://github.com/h0pe-ay/hooktechnology/blob/main/processhidden/detourshook.c
您想发表意见!!点此发布评论






发表评论