C++17文件系统库之std::filesystem 示例详解
150人参与 • 2025-03-07 • C/C++

前言
在c++编程中,文件系统操作是许多应用程序的基础功能之一。无论是读写文件、创建目录,还是遍历文件系统,文件系统操作几乎无处不在。然而,在c++17之前,标准库并没有提供一个统一、高效且易用的文件系统操作接口。开发者们不得不依赖于平台特定的api,或者使用第三方库,这不仅增加了代码的复杂性,也降低了代码的可移植性。
c++17引入了std::filesystem库,这是一个全新的文件系统操作库,旨在提供一个跨平台、高效且易用的文件系统操作接口。通过std::filesystem,开发者可以方便地进行文件和目录的操作,处理文件路径,获取文件属性等。这个库的引入极大地提升了c++在文件系统操作方面的能力,使得c++程序员能够更专注于业务逻辑的实现,而不必为平台差异和文件系统操作的细节烦恼。
本文将全面介绍std::filesystem库的功能和使用方法,通过丰富的代码示例和详细的解释,帮助读者快速掌握这一重要的c++17特性。
一、std::filesystem概述
std::filesystem是一个c++17新增的库,主要用于文件系统操作。它提供了一个跨平台的接口,允许开发者以统一的方式处理文件和目录操作。std::filesystem的核心在于其path类和filesystem命名空间中的各种函数,这些函数可以帮助我们完成文件和目录的创建、删除、复制、移动等操作。
std::filesystem的主要特点包括:
- 跨平台支持:
std::filesystem能够在多个平台上工作,包括windows、linux和macos。 - 异常处理:
std::filesystem提供了基于异常的错误处理机制,简化了错误处理流程。 - 高效性:
std::filesystem的实现非常高效,能够处理大规模的文件系统操作。 - 现代c++特性:
std::filesystem充分利用了c++11及以后的特性,如auto、decltype、move语义等。
二、核心功能详解
1. 文件和目录操作
std::filesystem提供了丰富的文件和目录操作接口,包括文件的创建、删除、复制、移动等。以下是一些常用的函数:
exists(): 检查文件或目录是否存在。create_directories(): 创建目录,包括父目录。remove(): 删除文件或目录。copy(): 复制文件或目录。rename(): 重命名文件或目录。resize_file(): 调整文件大小。
示例:创建目录和文件
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
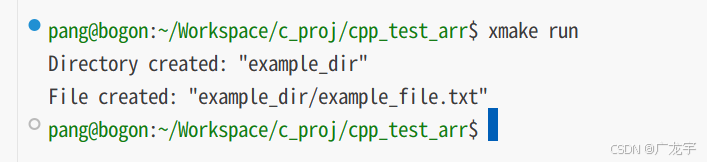
// 创建一个目录
fs::path dir_path("example_dir");
if (!fs::exists(dir_path)) {
fs::create_directories(dir_path);
std::cout << "directory created: " << dir_path << std::endl;
}
// 创建一个文件
fs::path file_path("example_dir/example_file.txt");
if (!fs::exists(file_path)) {
std::ofstream(file_path).close();
std::cout << "file created: " << file_path << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
2. 路径操作
std::filesystem提供了path类来处理文件路径。path类允许我们以一种平台无关的方式处理文件路径,例如提取文件名、扩展名、父路径等。
filename(): 获取文件名。extension(): 获取文件扩展名。parent_path(): 获取父路径。root_name(): 获取根名称(如windows上的驱动器号)。relative(): 获取相对路径。lexically_normal(): 规范化路径。
示例:路径操作
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
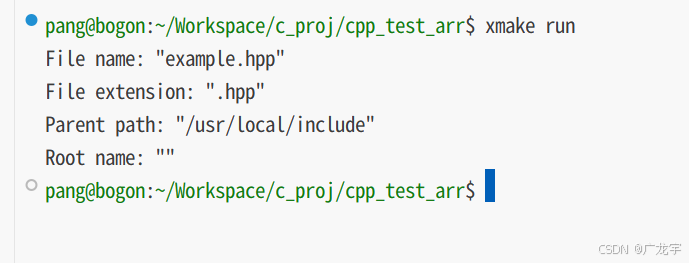
int main() {
fs::path path("/usr/local/include/example.hpp");
std::cout << "file name: " << path.filename() << std::endl;
std::cout << "file extension: " << path.extension() << std::endl;
std::cout << "parent path: " << path.parent_path() << std::endl;
std::cout << "root name: " << path.root_name() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
3. 文件属性操作
std::filesystem提供了多种函数来获取文件的属性,例如文件大小、文件类型、权限等。
file_size(): 获取文件大小。is_regular_file(): 检查是否是普通文件。is_directory(): 检查是否是目录。last_write_time(): 获取文件的最后写入时间。permissions(): 获取文件权限。
示例:获取文件属性
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
fs::path file_path("example_file.txt");
if (fs::exists(file_path)) {
if (fs::is_regular_file(file_path)) {
std::cout << "file size: " << fs::file_size(file_path) << " bytes" << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}4. 遍历目录
std::filesystem提供了directory_iterator和recursive_directory_iterator来遍历目录。directory_iterator用于遍历当前目录,而recursive_directory_iterator用于递归遍历目录。
directory_iterator: 遍历目录。recursive_directory_iterator: 递归遍历目录。
示例:遍历目录
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
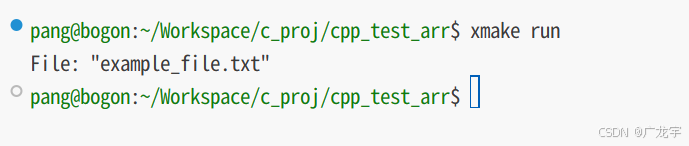
int main() {
fs::path dir_path("example_dir");
if (fs::exists(dir_path)) {
for (const auto& entry : fs::directory_iterator(dir_path)) {
if (fs::is_regular_file(entry.path())) {
std::cout << "file: " << entry.path().filename() << std::endl;
} else if (fs::is_directory(entry.path())) {
std::cout << "directory: " << entry.path().filename() << std::endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
5. 对现代c++的支持
std::filesystem充分利用了现代c++的特性,例如auto、decltype、move语义等。
示例:使用auto和decltype
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
auto path = fs::current_path();
decltype(path) dir_path = path / "example_dir";
if (!fs::exists(dir_path)) {
fs::create_directories(dir_path);
std::cout << "directory created: " << dir_path << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}6. 异常处理
std::filesystem提供了基于异常的错误处理机制。文件系统操作可能会抛出filesystem_error异常。
filesystem_error: 文件系统操作异常。
示例:异常处理
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
fs::path file_path("example_file.txt");
try {
if (fs::exists(file_path)) {
fs::remove(file_path);
std::cout << "file removed: " << file_path << std::endl;
}
} catch (const fs::filesystem_error& e) {
std::cerr << "error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}7. 跨平台支持
std::filesystem能够在多个平台上工作,包括windows、linux和macos。它能够处理不同平台的文件系统差异,例如路径分隔符、权限等。
示例:跨平台支持
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
fs::path path("example_dir/example_file.txt");
if (fs::exists(path)) {
std::cout << "file exists: " << path << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "file does not exist: " << path << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}总结
std::filesystem是c++17引入的一个强大且易用的文件系统操作库。它提供了跨平台的文件系统操作接口,简化了文件和目录操作的代码实现。通过std::filesystem,开发者可以高效、安全地处理文件系统操作,同时利用现代c++的特性,提升代码的可读性和可维护性。
在本文中,我们详细介绍了std::filesystem的核心功能,包括文件和目录操作、路径操作、文件属性操作、遍历目录、对现代c++的支持、异常处理以及跨平台支持。通过丰富的代码示例,我们展示了如何在实际项目中使用std::filesystem库。
希望本文能够帮助读者快速掌握std::filesystem的使用,并在实际开发中发挥其潜力。
到此这篇关于c++17文件系统库之std::filesystem 示例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c++文件系统库 std::filesystem内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!
您想发表意见!!点此发布评论





发表评论