MongoDB查询文档的各种技巧和最佳实践
102人参与 • 2025-10-18 • mongodb
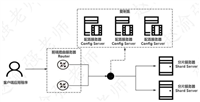
1. mongodb查询架构总览
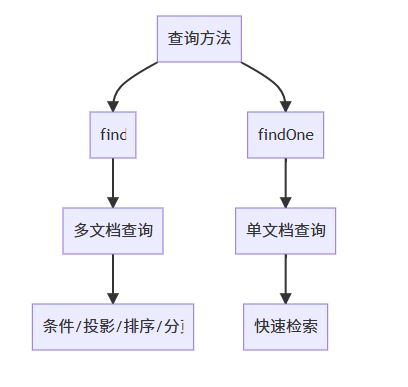
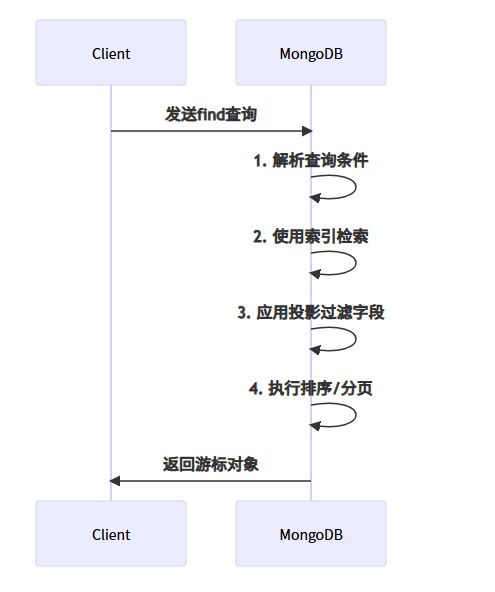
2. 核心查询方法详解
2.1 find()方法 - 多文档查询
基本语法:
db.collection.find( <query>, // 查询条件 <projection> // 投影(字段控制) ).<cursor_methods>() // 游标方法
典型查询流程:
2.2 findone()方法 - 单文档查询
特点对比:
| 特性 | find() | findone() |
|---|---|---|
| 返回结果 | 游标对象 | 文档对象/null |
| 性能 | 需迭代获取结果 | 立即返回单个结果 |
| 适用场景 | 批量数据检索 | 主键或唯一条件查询 |
// 示例:用户登录查询
const user = db.users.findone(
{ username: "alice123" },
{ password: 0 } // 排除密码字段
);
3. 查询条件深度解析
3.1 比较操作符大全
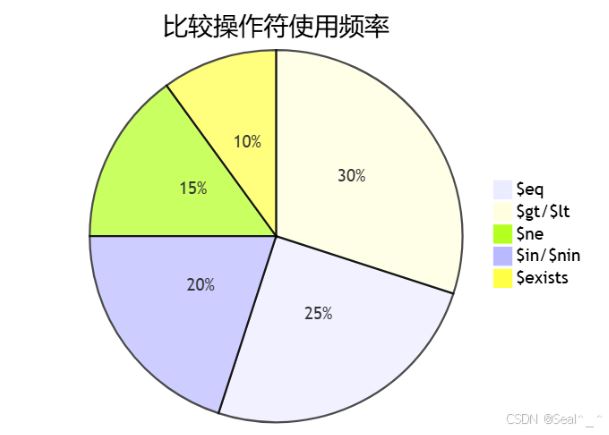
实际应用示例:
// 范围查询
db.products.find({
price: { $gt: 100, $lte: 500 },
stock: { $exists: true }
});
// 数组查询
db.users.find({
tags: { $in: ["vip", "premium"] },
age: { $nin: [18, 19, 20] }
});
3.2 逻辑操作符组合
复杂条件构建:
// and/or/not组合
db.orders.find({
$and: [
{ status: "completed" },
{ $or: [
{ payment: "credit" },
{ amount: { $gt: 1000 } }
]},
{ $not: { usertype: "trial" } }
]
});
4. 高级查询技巧
4.1 聚合管道查询

实际应用:
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $match: { date: { $gte: new date("2023-01-01") } } },
{ $project: { product: 1, total: { $multiply: ["$price", "$quantity"] } } },
{ $group: { _id: "$product", totalsales: { $sum: "$total" } } },
{ $sort: { totalsales: -1 } },
{ $limit: 10 }
]);
4.2 索引优化策略
索引使用原则:
esr规则:
- e (equality) 等值查询字段
- s (sort) 排序字段
- r (range) 范围查询字段
覆盖查询:
// 创建复合索引
db.users.createindex({ age: 1, status: 1 });
// 覆盖查询示例
db.users.find(
{ age: { $gt: 25 }, status: "active" },
{ _id: 0, age: 1, status: 1 }
).explain("executionstats");
5. 查询结果处理
5.1 游标控制方法
| 方法 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| sort() | 结果排序 | .sort({ age: -1 }) |
| limit() | 限制数量 | .limit(10) |
| skip() | 跳过文档 | .skip(20) |
| count() | 文档计数 | .count() |
| pretty() | 格式化输出 | .pretty() |
5.2 分页查询实现
// 分页函数
function paginate(collection, query, page = 1, pagesize = 10) {
const skip = (page - 1) * pagesize;
return {
data: collection.find(query).skip(skip).limit(pagesize).toarray(),
total: collection.countdocuments(query),
page,
pagesize
};
}
// 使用示例
const result = paginate(db.products, { category: "electronics" }, 2);
6. 生产环境最佳实践
6.1 查询性能优化
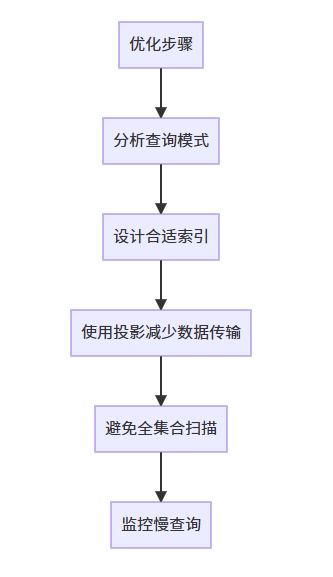
6.2 安全查询规范
- 查询注入防护:
// 不安全
const query = eval(`({ ${userinput} })`);
// 安全做法
const query = { status: userinputstatus };
- 结果大小限制:
// 设置最大返回文档大小
db.runcommand({ setparameter: 1, maxbsonsize: 16777216 });
// 查询时添加硬限制
db.logs.find().limit(1000);
7. 特殊查询场景
7.1 全文检索
// 创建文本索引
db.articles.createindex({ content: "text" });
// 文本搜索查询
db.articles.find(
{ $text: { $search: "mongodb tutorial" } },
{ score: { $meta: "textscore" } }
).sort({ score: { $meta: "textscore" } });
7.2 地理空间查询
// 创建2dsphere索引
db.places.createindex({ location: "2dsphere" });
// 附近地点查询
db.places.find({
location: {
$near: {
$geometry: {
type: "point",
coordinates: [longitude, latitude]
},
$maxdistance: 1000 // 1公里内
}
}
});
8. 性能监控与诊断
8.1 explain() 分析
// 获取查询执行计划
const explanation = db.orders
.find({ status: "shipped", amount: { $gt: 100 } })
.explain("executionstats");
// 关键指标解读
console.log({
executiontime: explanation.executionstats.executiontimemillis,
totaldocsexamined: explanation.executionstats.totaldocsexamined,
indexused: explanation.executionstats.executionstages.inputstage.indexname
});
8.2 慢查询日志
// 启用慢查询日志
db.setprofilinglevel(1, 50); // 记录>50ms的操作
// 分析慢查询
db.system.profile
.find({ op: "query", millis: { $gt: 100 } })
.sort({ ts: -1 })
.limit(10);
通过本文的全面介绍,您应该已经掌握了mongodb查询文档的各种技巧和最佳实践。合理设计查询条件、使用适当的索引并遵循性能优化原则,可以显著提升查询效率和应用响应速度。
以上就是mongodb查询文档的各种技巧和最佳实践的详细内容,更多关于mongodb查询文档的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!
赞 (0)
您想发表意见!!点此发布评论





发表评论