目标检测:如何将VOC标注的xml数据转为YOLO标注的txt格式,且生成classes的txt文件
289人参与 • 2024-07-31 • 车联网
1. 前言
目标检测数据的标注分为两种格式:
- xml 解释性标签,左上角+右下角的坐标
- txt 记事本文件,类别+x,y中心坐标+w,h的相对值
如下:
xml 文件格式:

txt 文件格式:
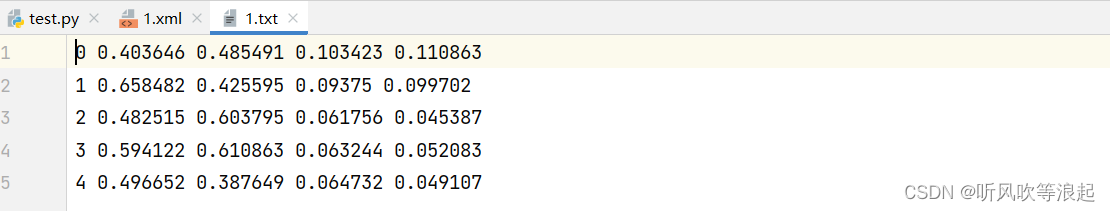
本文要实现的目标是将目标检测xml标注格式转为txt相对坐标的标注方式
所以本文,将根据voc标注的xml文件生成yolo格式的txt文件,且生成yolo需要的类别txt文件
2. 代码实现
简单介绍代码逻辑
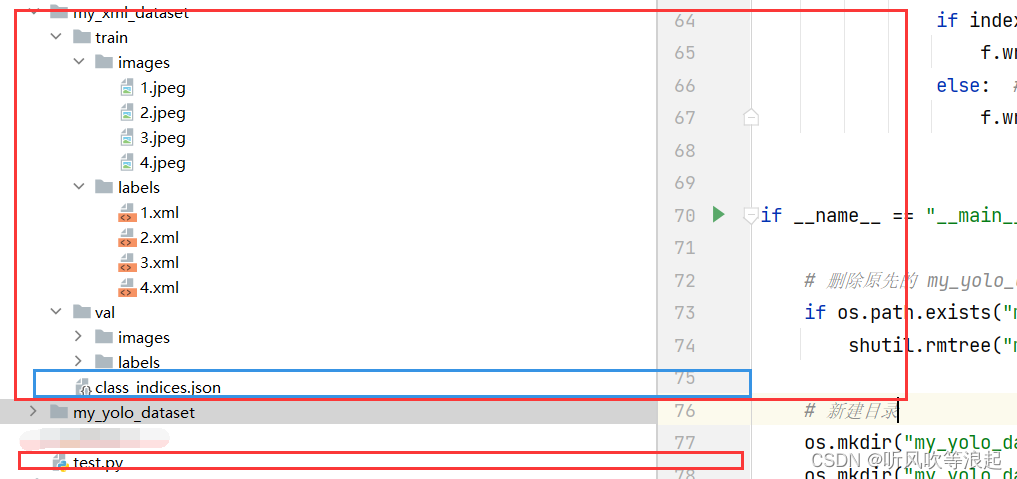
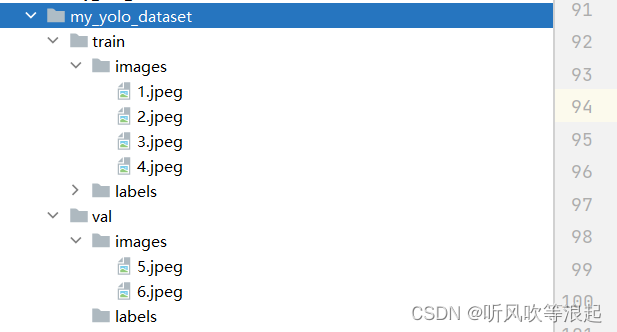
2.1 目录
目录结构:
这里是根据voc的训练集和验证集转换,且需要xml对应的json字典文件
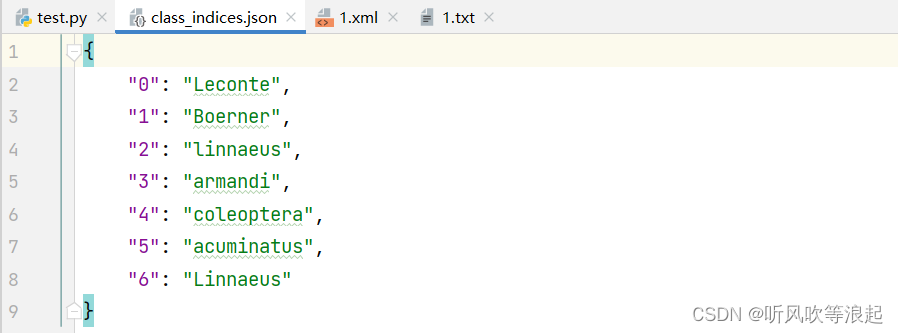
class_indices.json 如下:
没有的话,看这个自己生成:
2.2 图像的生成
关于图片,可以直接拷贝过去就行
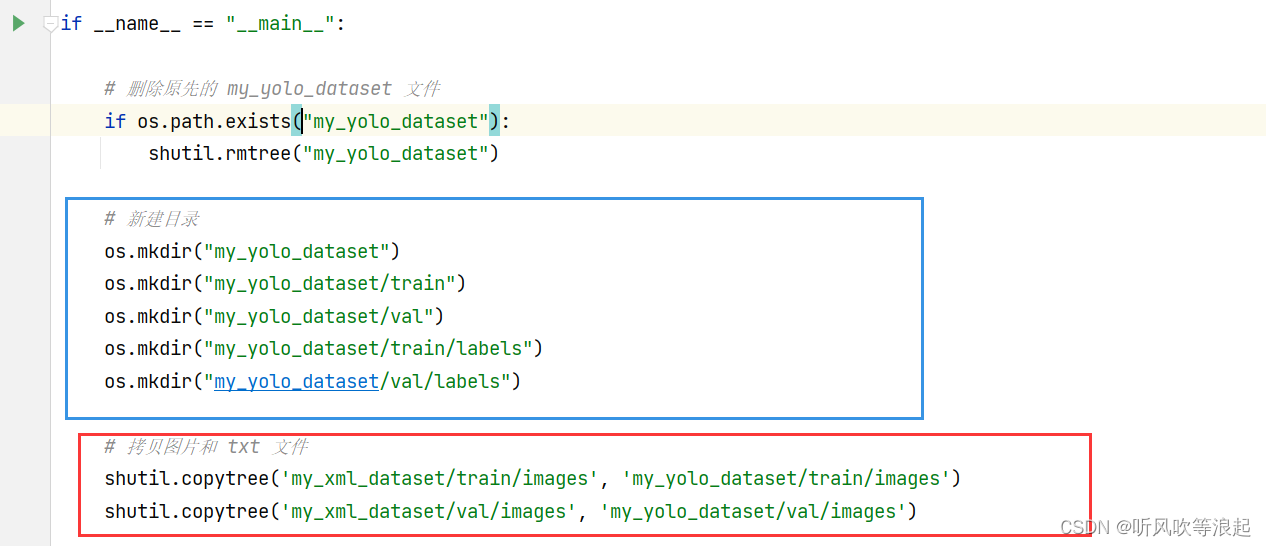
代码运行到这,可以看到图像已经拷贝过去
2.3 目标类别的txt文件生成
yolo格式的classes文件,这里默认根据voc的json字典文件生成,代码如下
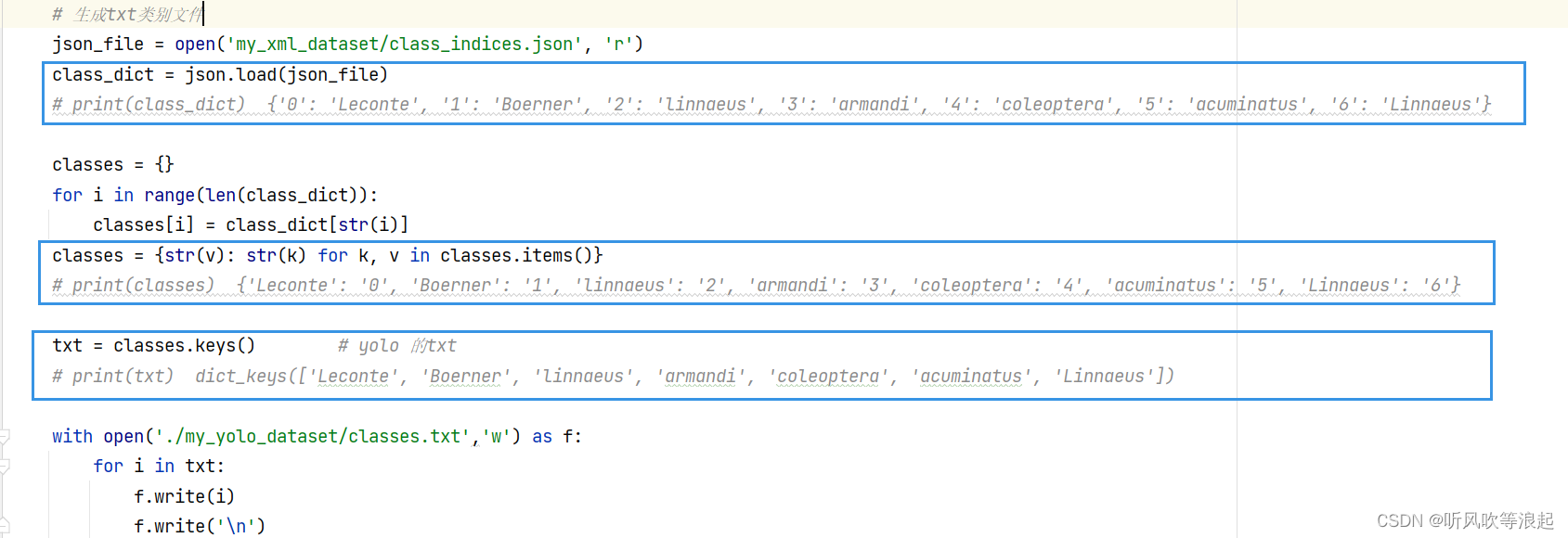
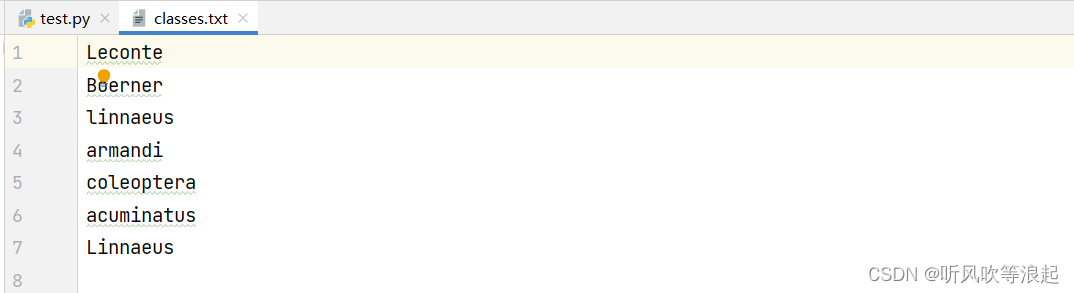
代码很简单,就是读取xml的json文件,获取字典的value值,然后保存在txt文件中
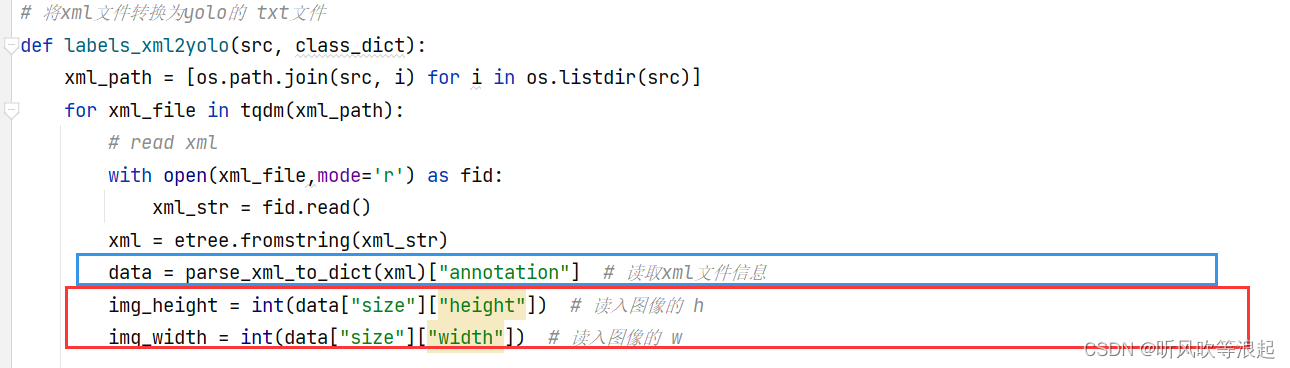
2.4 标签xml to yolo标签txt
这里通过labels_xml2yolo 自定义函数操作,传入训练集和验证集的xml目录即可,因为yolo的txt文件需要类别索引,这里将字典文件也传进去

这里需要保存原始图像的w、h,因为yolo标注是相对值,后面运算需要。因为voc标注的xml文件中包含了图像的size,直接读取即可
下面是将bbox坐标转为yolo相对坐标的代码,最终的数据就是info的存放的内容
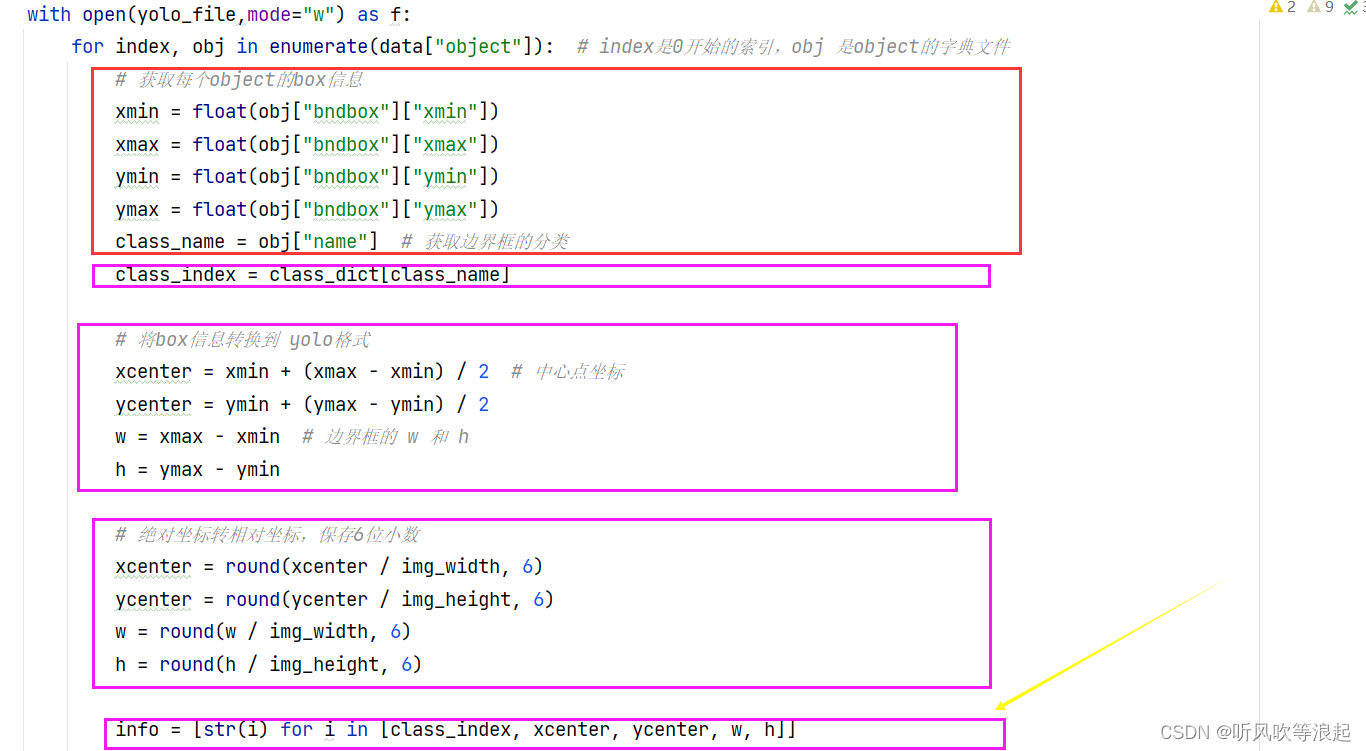
将info 保存即可
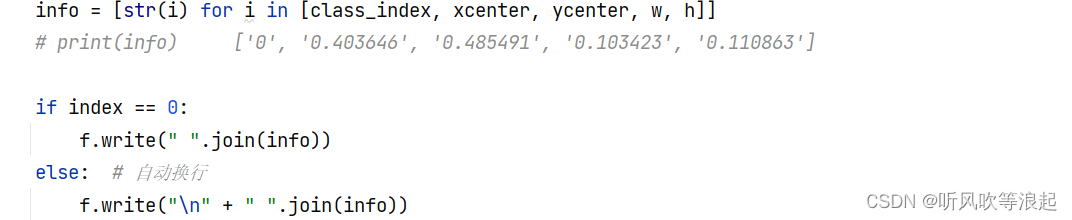
生成好的数据:
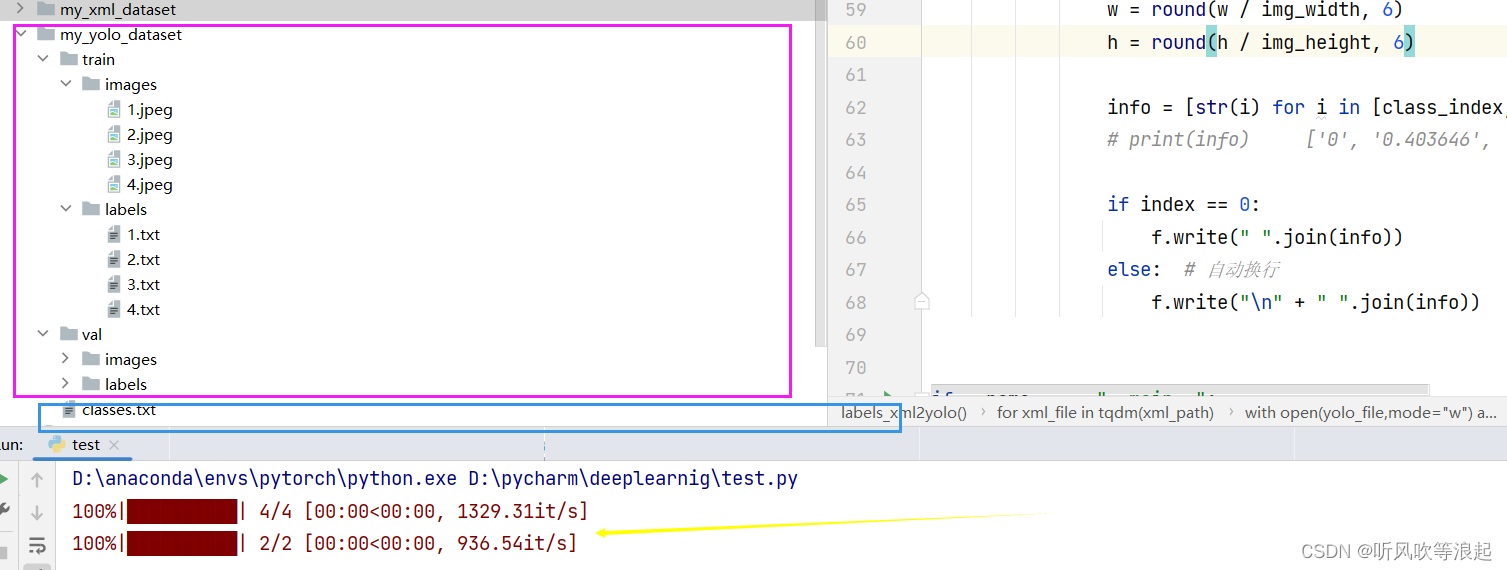
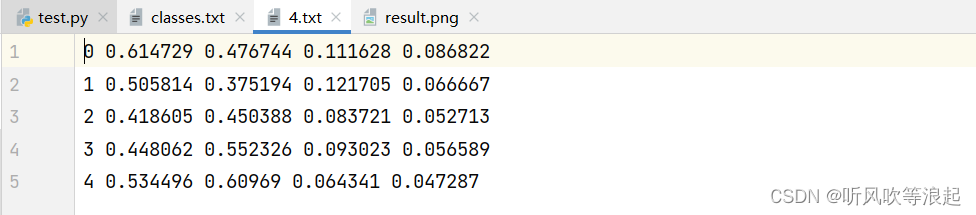
2.5 可视化
为了验证是否转化成功,利用 可视化一下

3. 完整代码
如下:
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
from lxml import etree
import shutil
import json
# 读取 xml 文件信息,并返回字典形式
def parse_xml_to_dict(xml):
if len(xml) == 0: # 遍历到底层,直接返回 tag对应的信息
return {xml.tag: xml.text}
result = {}
for child in xml:
child_result = parse_xml_to_dict(child) # 递归遍历标签信息
if child.tag != 'object':
result[child.tag] = child_result[child.tag]
else:
if child.tag not in result: # 因为object可能有多个,所以需要放入列表里
result[child.tag] = []
result[child.tag].append(child_result[child.tag])
return {xml.tag: result}
# 将xml文件转换为yolo的 txt文件
def labels_xml2yolo(src, class_dict):
xml_path = [os.path.join(src, i) for i in os.listdir(src)]
for xml_file in tqdm(xml_path):
# read xml
with open(xml_file,mode='r') as fid:
xml_str = fid.read()
xml = etree.fromstring(xml_str)
data = parse_xml_to_dict(xml)["annotation"] # 读取xml文件信息
img_height = int(data["size"]["height"]) # 读入图像的 h
img_width = int(data["size"]["width"]) # 读入图像的 w
# 新建 xml对应的 yolo txt标注文件,并写入
yolo_file = xml_file.replace('my_xml_dataset', 'my_yolo_dataset')
yolo_file = yolo_file.replace('.xml', '.txt')
with open(yolo_file,mode="w") as f:
for index, obj in enumerate(data["object"]): # index是0开始的索引,obj 是object的字典文件
# 获取每个object的box信息
xmin = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmin"])
xmax = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmax"])
ymin = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymin"])
ymax = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymax"])
class_name = obj["name"] # 获取边界框的分类
class_index = class_dict[class_name]
# 将box信息转换到 yolo格式
xcenter = xmin + (xmax - xmin) / 2 # 中心点坐标
ycenter = ymin + (ymax - ymin) / 2
w = xmax - xmin # 边界框的 w 和 h
h = ymax - ymin
# 绝对坐标转相对坐标,保存6位小数
xcenter = round(xcenter / img_width, 6)
ycenter = round(ycenter / img_height, 6)
w = round(w / img_width, 6)
h = round(h / img_height, 6)
info = [str(i) for i in [class_index, xcenter, ycenter, w, h]]
# print(info) ['0', '0.403646', '0.485491', '0.103423', '0.110863']
if index == 0:
f.write(" ".join(info))
else: # 自动换行
f.write("\n" + " ".join(info))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 删除原先的 my_yolo_dataset 文件
if os.path.exists("my_yolo_dataset"):
shutil.rmtree("my_yolo_dataset")
# 新建目录
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/train")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/val")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/train/labels")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/val/labels")
# 拷贝图片和 txt 文件
shutil.copytree('my_xml_dataset/train/images', 'my_yolo_dataset/train/images')
shutil.copytree('my_xml_dataset/val/images', 'my_yolo_dataset/val/images')
# 生成txt类别文件
json_file = open('my_xml_dataset/class_indices.json', 'r')
class_dict = json.load(json_file)
# print(class_dict) {'0': 'leconte', '1': 'boerner', '2': 'linnaeus', '3': 'armandi', '4': 'coleoptera', '5': 'acuminatus', '6': 'linnaeus'}
classes = {}
for i in range(len(class_dict)):
classes[i] = class_dict[str(i)]
classes = {str(v): str(k) for k, v in classes.items()}
# print(classes) {'leconte': '0', 'boerner': '1', 'linnaeus': '2', 'armandi': '3', 'coleoptera': '4', 'acuminatus': '5', 'linnaeus': '6'}
txt = classes.keys() # yolo 的txt
# print(txt) dict_keys(['leconte', 'boerner', 'linnaeus', 'armandi', 'coleoptera', 'acuminatus', 'linnaeus'])
with open('./my_yolo_dataset/classes.txt','w') as f:
for i in txt:
f.write(i)
f.write('\n')
# 将xml 标注信息更改为 yolo 格式
labels_xml2yolo(src='my_xml_dataset/train/labels', class_dict=classes)
labels_xml2yolo(src='my_xml_dataset/val/labels', class_dict=classes)
4. 附加代码
如果xml文件没有图片的size信息,用这个代码,会自动读取图片高度和宽度。并且会剔除xml文件种没有目标的部分
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
from lxml import etree
import shutil
import json
import cv2
# 读取 xml 文件信息,并返回字典形式
def parse_xml_to_dict(xml):
if len(xml) == 0: # 遍历到底层,直接返回 tag对应的信息
return {xml.tag: xml.text}
result = {}
for child in xml:
child_result = parse_xml_to_dict(child) # 递归遍历标签信息
if child.tag != 'object':
result[child.tag] = child_result[child.tag]
else:
if child.tag not in result: # 因为object可能有多个,所以需要放入列表里
result[child.tag] = []
result[child.tag].append(child_result[child.tag])
return {xml.tag: result}
# 将xml文件转换为yolo的 txt文件
def labels_xml2yolo(src, class_dict):
xml_path = [os.path.join(src, i) for i in os.listdir(src)]
for xml_file in tqdm(xml_path):
# read xml
with open(xml_file, mode='r') as fid:
xml_str = fid.read()
xml = etree.fromstring(xml_str)
data = parse_xml_to_dict(xml)["annotation"] # 读取xml文件信息
if 'object' not in data.keys(): # 移除不存在边界框的数据
continue
# 读取图片
img_path = xml_file.replace('labels','images')
img_path = img_path.replace('.xml','.jpg') # 根据后缀更换
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img_height,img_width = img.shape[:2]
# 新建 xml对应的 yolo txt标注文件,并写入
yolo_file = xml_file.replace('data', 'my_yolo_dataset')
yolo_file = yolo_file.replace('.xml', '.txt')
with open(yolo_file, mode="w") as f:
for index, obj in enumerate(data["object"]): # index是0开始的索引,obj 是object的字典文件
# 拷贝图片
shutil.copy(img_path, src.replace('data','my_yolo_dataset').replace('labels','images'))
# 获取每个object的box信息
xmin = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmin"])
xmax = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmax"])
ymin = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymin"])
ymax = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymax"])
class_name = obj["label"] # 获取边界框的分类
class_index = class_dict[class_name]
# 将box信息转换到 yolo格式
xcenter = xmin + (xmax - xmin) / 2 # 中心点坐标
ycenter = ymin + (ymax - ymin) / 2
w = xmax - xmin # 边界框的 w 和 h
h = ymax - ymin
# 绝对坐标转相对坐标,保存6位小数
xcenter = round(xcenter / img_width, 6)
ycenter = round(ycenter / img_height, 6)
w = round(w / img_width, 6)
h = round(h / img_height, 6)
info = [str(i) for i in [class_index, xcenter, ycenter, w, h]]
# print(info) ['0', '0.403646', '0.485491', '0.103423', '0.110863']
if index == 0:
f.write(" ".join(info))
else: # 自动换行
f.write("\n" + " ".join(info))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 删除原先的 my_yolo_dataset 文件
if os.path.exists("my_yolo_dataset"):
shutil.rmtree("my_yolo_dataset")
# 新建目录
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/train")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/test")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/train/labels")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/train/images")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/test/labels")
os.mkdir("my_yolo_dataset/test/images")
# 生成txt类别文件
json_file = open('class_indices.json', 'r')
class_dict = json.load(json_file)
# print(class_dict) {'0': 'leconte', '1': 'boerner', '2': 'linnaeus', '3': 'armandi', '4': 'coleoptera', '5': 'acuminatus', '6': 'linnaeus'}
classes = {}
for i in range(len(class_dict)):
classes[i] = class_dict[str(i)]
classes = {str(v): str(k) for k, v in classes.items()}
# print(classes) {'leconte': '0', 'boerner': '1', 'linnaeus': '2', 'armandi': '3', 'coleoptera': '4', 'acuminatus': '5', 'linnaeus': '6'}
txt = classes.keys() # yolo 的txt
# print(txt) dict_keys(['leconte', 'boerner', 'linnaeus', 'armandi', 'coleoptera', 'acuminatus', 'linnaeus'])
with open('./my_yolo_dataset/classes.txt', 'w') as f:
for i in txt:
f.write(i)
f.write('\n')
# 将xml 标注信息更改为 yolo 格式
labels_xml2yolo(src='data/train/labels', class_dict=classes)
labels_xml2yolo(src='data/test/labels', class_dict=classes)
您想发表意见!!点此发布评论




发表评论