SpringBoot——集成Kafka详解
40人参与 • 2024-07-28 • Java
springboot集成kafka
1、构建项目
1.1、引入依赖
<parent>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactid>
<version>2.2.5.release</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.kafka</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-kafka</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.projectlombok</groupid>
<artifactid>lombok</artifactid>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>com.alibaba</groupid>
<artifactid>fastjson</artifactid>
<version>1.2.28</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>junit</groupid>
<artifactid>junit</artifactid>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.2、application.yml配置
spring:
application:
name: application-kafka
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092 #这个是kafka的地址,对应你server.properties中配置的
producer:
batch-size: 16384 #批量大小
acks: -1 #应答级别:多少个分区副本备份完成时向生产者发送ack确认(可选0、1、all/-1)
retries: 10 # 消息发送重试次数
#transaction-id-prefix: transaction
buffer-memory: 33554432
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.stringserializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.stringserializer
properties:
linger:
ms: 2000 #提交延迟
#partitioner: #指定分区器
#class: pers.zhang.config.customerpartitionhandler
consumer:
group-id: testgroup #默认的消费组id
enable-auto-commit: true #是否自动提交offset
auto-commit-interval: 2000 #提交offset延时
# 当kafka中没有初始offset或offset超出范围时将自动重置offset
# earliest:重置为分区中最小的offset;
# latest:重置为分区中最新的offset(消费分区中新产生的数据);
# none:只要有一个分区不存在已提交的offset,就抛出异常;
auto-offset-reset: latest
max-poll-records: 500 #单次拉取消息的最大条数
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.stringdeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.stringdeserializer
properties:
session:
timeout:
ms: 120000 # 消费会话超时时间(超过这个时间 consumer 没有发送心跳,就会触发 rebalance 操作)
request:
timeout:
ms: 18000 # 消费请求的超时时间
listener:
missing-topics-fatal: false # consumer listener topics 不存在时,启动项目就会报错
# type: batch
1.3、简单生产
@restcontroller
public class kafkaproducer {
@autowired
private kafkatemplate<string, object> kafkatemplate;
@getmapping("/kafka/normal/{message}")
public void sendnormalmessage(@pathvariable("message") string message) {
kafkatemplate.send("sb_topic", message);
}
}
1.4、简单消费
@component
public class kafkaconsumer {
//监听消费
@kafkalistener(topics = {"sb_topic"})
public void onnormalmessage(consumerrecord<string, object> record) {
system.out.println("简单消费:" + record.topic() + "-" + record.partition() + "=" +
record.value());
}
}
简单消费:sb_topic-0=111
简单消费:sb_topic-0=222
简单消费:sb_topic-0=333
2、生产者
2.1、带回调的生产者
kafkatemplate提供了一个回调方法addcallback,我们可以在回调方法中监控消息是否发送成功 或 失败时做补偿处理,有两种写法,
/**
* 回调的第一种写法
* @param message
*/
@getmapping("/kafka/callbackone/{message}")
public void sendcallbackonemessage(@pathvariable("message") string message) {
kafkatemplate.send("sb_topic", message).addcallback(new successcallback<sendresult<string, object>>() {
//成功的回调
@override
public void onsuccess(sendresult<string, object> success) {
// 消息发送到的topic
string topic = success.getrecordmetadata().topic();
// 消息发送到的分区
int partition = success.getrecordmetadata().partition();
// 消息在分区内的offset
long offset = success.getrecordmetadata().offset();
system.out.println("发送消息成功1:" + topic + "-" + partition + "-" + offset);
}
}, new failurecallback() {
//失败的回调
@override
public void onfailure(throwable throwable) {
system.out.println("发送消息失败1:" + throwable.getmessage());
}
});
}

发送消息成功1:sb_topic-0-3
简单消费:sb_topic-0=one
/**
* 回调的第二种写法
* @param message
*/
@getmapping("/kafka/callbacktwo/{message}")
public void sendcallbacktwomessage(@pathvariable("message") string message) {
kafkatemplate.send("sb_topic", message).addcallback(new listenablefuturecallback<sendresult<string, object>>() {
@override
public void onfailure(throwable throwable) {
system.out.println("发送消息失败2:"+throwable.getmessage());
}
@override
public void onsuccess(sendresult<string, object> result) {
system.out.println("发送消息成功2:" + result.getrecordmetadata().topic() + "-"
+ result.getrecordmetadata().partition() + "-" + result.getrecordmetadata().offset());
}
});
}
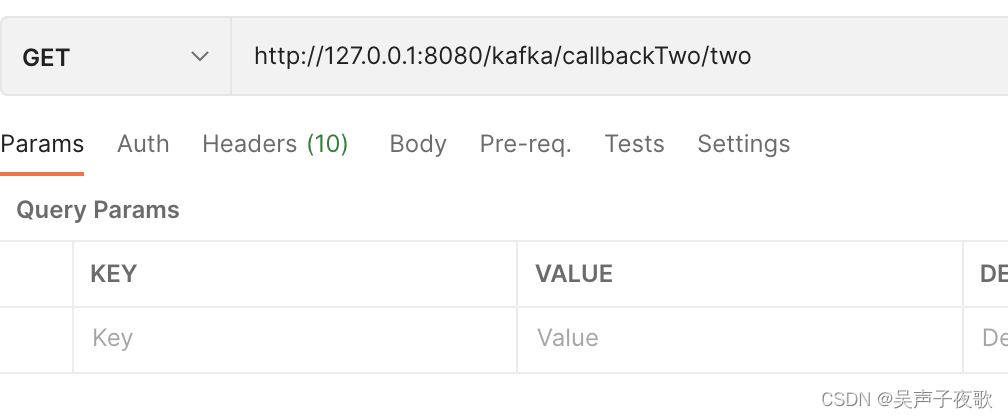
发送消息成功2:sb_topic-0-4
简单消费:sb_topic-0=two
2.2、监听器
kafka提供了producerlistener 监听器来异步监听生产者消息是否发送成功,我们可以自定义一个kafkatemplate添加producerlistener,当消息发送失败我们可以拿到消息进行重试或者把失败消息记录到数据库定时重试。
@configuration
public class kafkaconfig {
@autowired
producerfactory producerfactory;
@bean
public kafkatemplate<string, object> kafkatemplate() {
kafkatemplate<string, object> kafkatemplate = new kafkatemplate<string, object>();
kafkatemplate.setproducerlistener(new producerlistener<string, object>() {
@override
public void onsuccess(producerrecord<string, object> producerrecord, recordmetadata recordmetadata) {
system.out.println("发送成功 " + producerrecord.tostring());
}
@override
public void onsuccess(string topic, integer partition, string key, object value, recordmetadata recordmetadata) {
system.out.println("发送成功 topic = " + topic + " ; partion = " + partition + "; key = " + key + " ; value=" + value);
}
@override
public void onerror(producerrecord<string, object> producerrecord, exception exception) {
system.out.println("发送失败" + producerrecord.tostring());
system.out.println(exception.getmessage());
}
@override
public void onerror(string topic, integer partition, string key, object value, exception exception) {
system.out.println("发送失败" + "topic = " + topic + " ; partion = " + partition + "; key = " + key + " ; value=" + value);
system.out.println(exception.getmessage());
}
});
return kafkatemplate;
}
}
注意:当我们发送一条消息,既会走 listenablefuturecallback 回调,也会走producerlistener回调。
2.3、自定义分区器
我们知道,kafka中每个topic被划分为多个分区,那么生产者将消息发送到topic时,具体追加到哪个分区呢?这就是所谓的分区策略,kafka 为我们提供了默认的分区策略,同时它也支持自定义分区策略。其路由机制为:
- 若发送消息时指定了分区(即自定义分区策略),则直接将消息append到指定分区;
- 若发送消息时未指定 patition,但指定了 key(kafka允许为每条消息设置一个key),则对key值进行hash计算,根据计算结果路由到指定分区,这种情况下可以保证同一个 key 的所有消息都进入到相同的分区;
- patition 和 key 都未指定,则使用kafka默认的分区策略,轮询选出一个 patition;
我们来自定义一个分区策略,将消息发送到我们指定的partition,首先新建一个分区器类实现partitioner接口,重写方法,其中partition方法的返回值就表示将消息发送到几号分区
public class customizepartitioner implements partitioner {
@override
public int partition(string s, object o, byte[] bytes, object o1, byte[] bytes1, cluster cluster) {
//自定义分区规则,默认全部发送到0号分区
return 0;
}
@override
public void close() {
}
@override
public void configure(map<string, ?> map) {
}
}
在application.properties中配置自定义分区器,配置的值就是分区器类的全路径名
# 自定义分区器
spring.kafka.producer.properties.partitioner.class=pers.zhang.config.customizepartitioner
2.4、事务提交
如果在发送消息时需要创建事务,可以使用 kafkatemplate 的 executeintransaction 方法来声明事务:
@getmapping("/kafka/transaction/{message}")
public void sendtransactionmessage(@pathvariable("message") string message) {
//声明事务:后面报错消息不会发出去
kafkatemplate.executeintransaction(new kafkaoperations.operationscallback<string, object, object>() {
@override
public object doinoperations(kafkaoperations<string, object> operations) {
operations.send("sb_topic", message + " test executeintransaction");
throw new runtimeexception("fail");
}
});
// //不声明事务:后面报错但前面消息已经发送成功了
// kafkatemplate.send("sb_topic", message + " test executeinnotransaction");
// throw new runtimeexception("fail");
}
注意:如果声明了事务,需要在application.yml中指定:
spring:
kafka:
producer:
transaction-id-prefix: tx_ #事务id前缀
3、消费者
3.1、指定topic、partition、offset消费
前面我们在监听消费topic1的时候,监听的是topic1上所有的消息,如果我们想指定topic、指定partition、指定offset来消费呢?也很简单,@kafkalistener注解已全部为我们提供
spring:
kafka:
listener:
type: batch #设置批量消费
consumer:
max-poll-records: 50 #每次最多消费多少条消息
属性解释:
id:消费者idgroupid:消费组idtopics:监听的topic,可监听多个topicpartitions:可配置更加详细的监听信息,可指定topic、parition、offset监听,手动分区。
//批量消费
@kafkalistener(id = "consumer2", topics = {"sb_topic"}, groupid = "sb_group")
public void onbatchmessage(list<consumerrecord<string, object>> records) {
system.out.println(">>> 批量消费一次,recoreds.size()=" + records.size());
for (consumerrecord<string, object> record : records) {
system.out.println(record.value());
}
}
>>> 批量消费一次,recoreds.size()=4
hello
hello
hello
hello
>>> 批量消费一次,recoreds.size()=2
hello
hello
3.2、异常处理
consumerawarelistenererrorhandler 异常处理器,新建一个 consumerawarelistenererrorhandler 类型的异常处理方法,用@bean注入,beanname默认就是方法名,然后我们将这个异常处理器的beanname放到@kafkalistener注解的errorhandler属性里面,当监听抛出异常的时候,则会自动调用异常处理器。
//异常处理器
@bean
public consumerawarelistenererrorhandler consumerawareerrorhandler() {
return new consumerawarelistenererrorhandler() {
@override
public object handleerror(message<?> message, listenerexecutionfailedexception exception, consumer<?, ?> consumer) {
system.out.println("消费异常:" + message.getpayload());
return null;
}
};
}
// 将这个异常处理器的beanname放到@kafkalistener注解的errorhandler属性里面
@kafkalistener(topics = {"sb_topic"},errorhandler = "consumerawareerrorhandler")
public void onmessage4(consumerrecord<?, ?> record) throws exception {
throw new exception("简单消费-模拟异常");
}
// 批量消费也一样,异常处理器的message.getpayload()也可以拿到各条消息的信息
@kafkalistener(topics = "sb_topic",errorhandler="consumerawareerrorhandler")
public void onmessage5(list<consumerrecord<?, ?>> records) throws exception {
system.out.println("批量消费一次...");
throw new exception("批量消费-模拟异常");
}
批量消费一次...
消费异常:[consumerrecord(topic = sb_topic, partition = 0, leaderepoch = 0, offset = 19, createtime = 1692604586558, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 5, headers = recordheaders(headers = [], isreadonly = false), key = null, value = hello), consumerrecord(topic = sb_topic, partition = 0, leaderepoch = 0, offset = 20, createtime = 1692604587164, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 5, headers = recordheaders(headers = [], isreadonly = false), key = null, value = hello), consumerrecord(topic = sb_topic, partition = 0, leaderepoch = 0, offset = 21, createtime = 1692604587790, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 5, headers = recordheaders(headers = [], isreadonly = false), key = null, value = hello)]
3.3、消息过滤器
消息过滤器可以在消息抵达consumer之前被拦截,在实际应用中,我们可以根据自己的业务逻辑,筛选出需要的信息再交由kafkalistener处理,不需要的消息则过滤掉。
配置消息过滤只需要为 监听器工厂 配置一个recordfilterstrategy(消息过滤策略),返回true的时候消息将会被抛弃,返回false时,消息能正常抵达监听容器。
@autowired
consumerfactory consumerfactory;
//消息过滤器
@bean
public concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory filtercontainerfactory() {
concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory factory = new concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory();
factory.setconsumerfactory(consumerfactory);
//被过滤的消息将被丢弃
factory.setackdiscarded(true);
//消息过滤策略
factory.setrecordfilterstrategy(new recordfilterstrategy() {
@override
public boolean filter(consumerrecord consumerrecord) {
if (integer.parseint(consumerrecord.value().tostring()) % 2 == 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
});
return factory;
}
//消息过滤监听
@kafkalistener(topics = {"sb_topic"},containerfactory = "filtercontainerfactory")
public void onmessage6(consumerrecord<?, ?> record) {
system.out.println(record.value());
}
上面实现了一个"过滤奇数、接收偶数"的过滤策略,我们向topic发送0-9总共10条消息,看一下监听器的消费情况,可以看到监听器只消费了偶数:
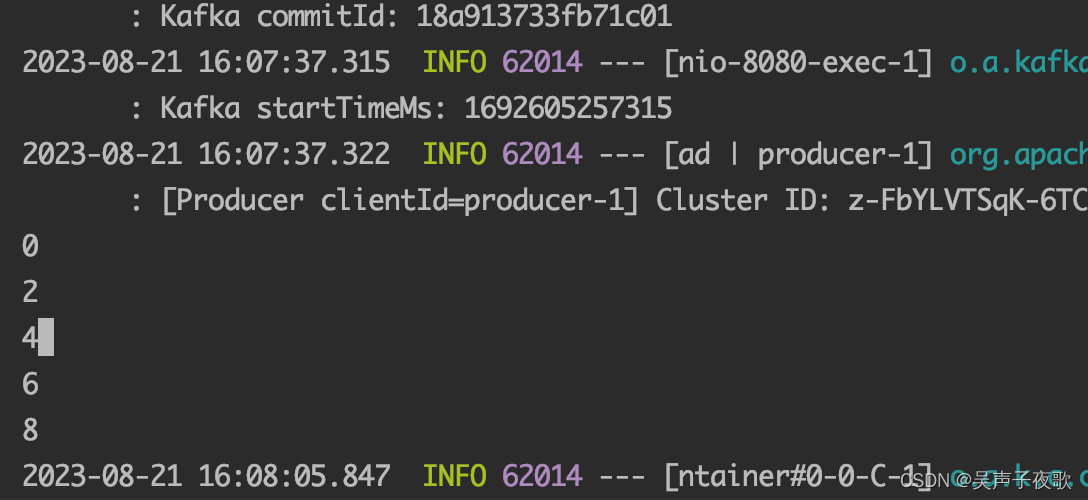
3.4、消息转发
在实际开发中,我们可能有这样的需求,应用a从topica获取到消息,经过处理后转发到topicb,再由应用b监听处理消息,即一个应用处理完成后将该消息转发至其他应用,完成消息的转发。
在springboot集成kafka实现消息的转发也很简单,只需要通过一个@sendto注解,被注解方法的return值即转发的消息内容,如下:
//消息转发 从sb_topic转发到sb_topic2
@kafkalistener(topics = {"sb_topic"})
@sendto("sb_topic2")
public string onmessage7(consumerrecord<?, ?> record) {
return record.value()+"-forward message";
}
@kafkalistener(topics = {"sb_topic2"})
public void onmessage8(consumerrecord<?, ?> record) {
system.out.println("收到sb_topic转发过来的消息:" + record.value());
}
收到sb_topic转发过来的消息:hello-forward message
收到sb_topic转发过来的消息:hello-forward message
收到sb_topic转发过来的消息:hello-forward message
收到sb_topic转发过来的消息:hello-forward message
3.5、定时启动、停止
默认情况下,当消费者项目启动的时候,监听器就开始工作,监听消费发送到指定topic的消息,那如果我们不想让监听器立即工作,想让它在我们指定的时间点开始工作,或者在我们指定的时间点停止工作,该怎么处理呢——使用kafkalistenerendpointregistry,下面我们就来实现:
- 禁止监听器自启动;
- 创建两个定时任务,一个用来在指定时间点启动定时器,另一个在指定时间点停止定时器;
新建一个定时任务类,用注解@enablescheduling声明,kafkalistenerendpointregistry 在spring中已经被注册为bean,直接注入,设置禁止kafkalistener自启动
@enablescheduling
@component
public class crontimer {
/**
* @kafkalistener注解所标注的方法并不会在ioc容器中被注册为bean,
* 而是会被注册在kafkalistenerendpointregistry中,
* 而kafkalistenerendpointregistry在springioc中已经被注册为bean
**/
@autowired
private kafkalistenerendpointregistry registry;
@autowired
private consumerfactory consumerfactory;
// 监听器容器工厂(设置禁止kafkalistener自启动)
@bean
public concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory delaycontainerfactory() {
concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory container = new concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory();
container.setconsumerfactory(consumerfactory);
//禁止kafkalistener自启动
container.setautostartup(false);
return container;
}
// 监听器
@kafkalistener(id="timingconsumer",topics = "sb_topic",containerfactory = "delaycontainerfactory")
public void onmessage1(consumerrecord<?, ?> record){
system.out.println("消费成功:"+record.topic()+"-"+record.partition()+"-"+record.value());
}
// 定时启动监听器
@scheduled(cron = "0 42 11 * * ? ")
public void startlistener() {
system.out.println("启动监听器...");
// "timingconsumer"是@kafkalistener注解后面设置的监听器id,标识这个监听器
if (!registry.getlistenercontainer("timingconsumer").isrunning()) {
registry.getlistenercontainer("timingconsumer").start();
}
//registry.getlistenercontainer("timingconsumer").resume();
}
// 定时停止监听器
@scheduled(cron = "0 45 11 * * ? ")
public void shutdownlistener() {
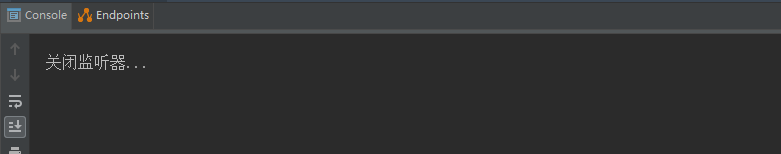
system.out.println("关闭监听器...");
registry.getlistenercontainer("timingconsumer").pause();
}
}
启动项目,触发生产者向topic1发送消息,可以看到consumer没有消费,因为这时监听器还没有开始工作,
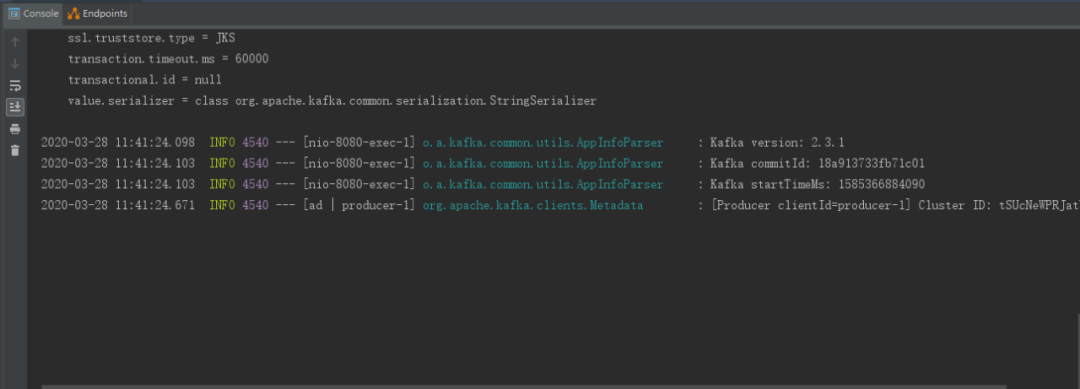
11:42分监听器启动开始工作,消费消息
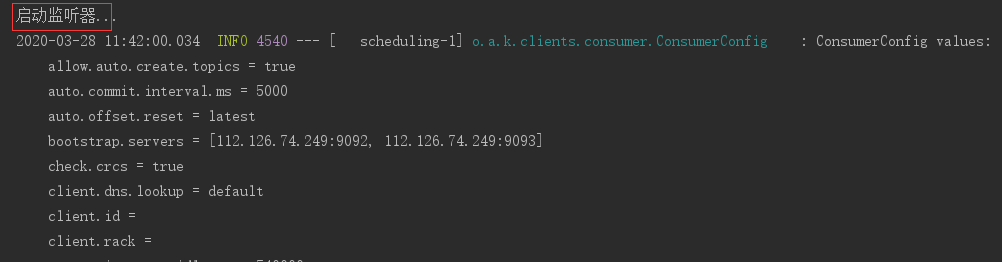
11:45分监听器停止工作:
3.6、手动确认消息
默认情况下kafka的消费者是自动确认消息的,通常情况下我们需要在业务处理成功之后手动触发消息的签收,否则可能会出现:消息消费到一半消费者异常,消息并未消费成功但是消息已经自动被确认,也不会再投递给消费者,也就导致消息丢失了。
当 auto.commit.enable 设置为false时,表示kafak的offset由customer手动维护,spring-kafka提供了通过ackmode的值表示不同的手动提交方式;
public enum ackmode {
// 当每一条记录被消费者监听器(listenerconsumer)处理之后提交
record,
// 当每一批poll()的数据被消费者监听器(listenerconsumer)处理之后提交
batch,
// 当每一批poll()的数据被消费者监听器(listenerconsumer)处理之后,距离上次提交时间大于time时提交
time,
// 当每一批poll()的数据被消费者监听器(listenerconsumer)处理之后,被处理record数量大于等于count时提交
count,
// time | count 有一个条件满足时提交
count_time,
// 当每一批poll()的数据被消费者监听器(listenerconsumer)处理之后, 手动调用acknowledgment.acknowledge()后提交
manual,
// 手动调用acknowledgment.acknowledge()后立即提交
manual_immediate,
}
如果设置ackmode模式为manual或者manual_immediate,则需要对监听消息的方法中,引入acknowledgment对象参数,并调用acknowledge()方法进行手动提交;
第一步:添加kafka配置,把 spring.kafka.listener.ack-mode = manual 设置为手动
spring:
kafka:
listener:
ack-mode: manual
consumer:
enable-auto-commit: false
第二步;消费消息的时候,给方法添加acknowledgment参数签收消息:
@kafkalistener(topics = {"sb_topic"})
public void onmessage9(consumerrecord<string, object> record, acknowledgment ack) {
system.out.println("收到消息:" + record.value());
//确认消息
ack.acknowledge();
}
4、配置详解
4.1、生产者yml方式
server:
port: 8081
spring:
kafka:
producer:
# kafka服务器
bootstrap-servers: 175.24.228.202:9092
# 开启事务,必须在开启了事务的方法中发送,否则报错
transaction-id-prefix: kafkatx-
# 发生错误后,消息重发的次数,开启事务必须设置大于0。
retries: 3
# acks=0 : 生产者在成功写入消息之前不会等待任何来自服务器的响应。
# acks=1 : 只要集群的首领节点收到消息,生产者就会收到一个来自服务器成功响应。
# acks=all :只有当所有参与复制的节点全部收到消息时,生产者才会收到一个来自服务器的成功响应。
# 开启事务时,必须设置为all
acks: all
# 当有多个消息需要被发送到同一个分区时,生产者会把它们放在同一个批次里。该参数指定了一个批次可以使用的内存大小,按照字节数计算。
batch-size: 16384
# 生产者内存缓冲区的大小。
buffer-memory: 1024000
# 键的序列化方式
key-serializer: org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.jsonserializer
# 值的序列化方式(建议使用json,这种序列化方式可以无需额外配置传输实体类)
value-serializer: org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.jsonserializer
4.2、生产者config方式
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.producerconfig;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.stringserializer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.value;
import org.springframework.boot.springbootconfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.defaultkafkaproducerfactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.kafkatemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.producerfactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.jsonserializer;
import org.springframework.kafka.transaction.kafkatransactionmanager;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
/**
* kafka配置,也可以写在yml,这个文件会覆盖yml
*/
@springbootconfiguration
public class kafkaproviderconfig {
@value("${spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers}")
private string bootstrapservers;
@value("${spring.kafka.producer.transaction-id-prefix}")
private string transactionidprefix;
@value("${spring.kafka.producer.acks}")
private string acks;
@value("${spring.kafka.producer.retries}")
private string retries;
@value("${spring.kafka.producer.batch-size}")
private string batchsize;
@value("${spring.kafka.producer.buffer-memory}")
private string buffermemory;
@bean
public map<string, object> producerconfigs() {
map<string, object> props = new hashmap<>(16);
props.put(producerconfig.bootstrap_servers_config, bootstrapservers);
//acks=0 : 生产者在成功写入消息之前不会等待任何来自服务器的响应。
//acks=1 : 只要集群的首领节点收到消息,生产者就会收到一个来自服务器成功响应。
//acks=all :只有当所有参与复制的节点全部收到消息时,生产者才会收到一个来自服务器的成功响应。
//开启事务必须设为all
props.put(producerconfig.acks_config, acks);
//发生错误后,消息重发的次数,开启事务必须大于0
props.put(producerconfig.retries_config, retries);
//当多个消息发送到相同分区时,生产者会将消息打包到一起,以减少请求交互. 而不是一条条发送
//批次的大小可以通过batch.size 参数设置.默认是16kb
//较小的批次大小有可能降低吞吐量(批次大小为0则完全禁用批处理)。
//比如说,kafka里的消息5秒钟batch才凑满了16kb,才能发送出去。那这些消息的延迟就是5秒钟
//实测batchsize这个参数没有用
props.put(producerconfig.batch_size_config, batchsize);
//有的时刻消息比较少,过了很久,比如5min也没有凑够16kb,这样延时就很大,所以需要一个参数. 再设置一个时间,到了这个时间,
//即使数据没达到16kb,也将这个批次发送出去
props.put(producerconfig.linger_ms_config, "5000");
//生产者内存缓冲区的大小
props.put(producerconfig.buffer_memory_config, buffermemory);
//反序列化,和生产者的序列化方式对应
props.put(producerconfig.key_serializer_class_config, jsonserializer.class);
props.put(producerconfig.value_serializer_class_config, jsonserializer.class);
return props;
}
@bean
public producerfactory<object, object> producerfactory() {
defaultkafkaproducerfactory<object, object> factory = new defaultkafkaproducerfactory<>(producerconfigs());
//开启事务,会导致 linger_ms_config 配置失效
factory.settransactionidprefix(transactionidprefix);
return factory;
}
@bean
public kafkatransactionmanager<object, object> kafkatransactionmanager(producerfactory<object, object> producerfactory) {
return new kafkatransactionmanager<>(producerfactory);
}
@bean
public kafkatemplate<object, object> kafkatemplate() {
return new kafkatemplate<>(producerfactory());
}
}
4.3、消费者yml方式
server:
port: 8082
spring:
kafka:
consumer:
# kafka服务器
bootstrap-servers: 175.24.228.202:9092
group-id: firstgroup
# 自动提交的时间间隔 在spring boot 2.x 版本中这里采用的是值的类型为duration 需要符合特定的格式,如1s,1m,2h,5d
#auto-commit-interval: 2s
# 该属性指定了消费者在读取一个没有偏移量的分区或者偏移量无效的情况下该作何处理:
# earliest:当各分区下有已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;无提交的offset时,从头开始消费分区的记录
# latest:当各分区下有已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;无提交的offset时,消费新产生的该分区下的数据(在消费者启动之后生成的记录)
# none:当各分区都存在已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;只要有一个分区不存在已提交的offset,则抛出异常
auto-offset-reset: latest
# 是否自动提交偏移量,默认值是true,为了避免出现重复数据和数据丢失,可以把它设置为false,然后手动提交偏移量
enable-auto-commit: false
# 键的反序列化方式
#key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.stringdeserializer
key-deserializer: org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.jsondeserializer
# 值的反序列化方式(建议使用json,这种序列化方式可以无需额外配置传输实体类)
value-deserializer: org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.jsondeserializer
# 配置消费者的 json 反序列化的可信赖包,反序列化实体类需要
properties:
spring:
json:
trusted:
packages: "*"
# 这个参数定义了poll方法最多可以拉取多少条消息,默认值为500。如果在拉取消息的时候新消息不足500条,那有多少返回多少;如果超过500条,每次只返回500。
# 这个默认值在有些场景下太大,有些场景很难保证能够在5min内处理完500条消息,
# 如果消费者无法在5分钟内处理完500条消息的话就会触发rebalance,
# 然后这批消息会被分配到另一个消费者中,还是会处理不完,这样这批消息就永远也处理不完。
# 要避免出现上述问题,提前评估好处理一条消息最长需要多少时间,然后覆盖默认的max.poll.records参数
# 注:需要开启batchlistener批量监听才会生效,如果不开启batchlistener则不会出现rebalance情况
max-poll-records: 3
properties:
# 两次poll之间的最大间隔,默认值为5分钟。如果超过这个间隔会触发rebalance
max:
poll:
interval:
ms: 600000
# 当broker多久没有收到consumer的心跳请求后就触发rebalance,默认值是10s
session:
timeout:
ms: 10000
listener:
# 在侦听器容器中运行的线程数,一般设置为 机器数*分区数
concurrency: 4
# 自动提交关闭,需要设置手动消息确认
ack-mode: manual_immediate
# 消费监听接口监听的主题不存在时,默认会报错,所以设置为false忽略错误
missing-topics-fatal: false
# 两次poll之间的最大间隔,默认值为5分钟。如果超过这个间隔会触发rebalance
poll-timeout: 600000
4.4、消费者config方式
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.consumerconfig;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.value;
import org.springframework.boot.springbootconfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.kafkalistenercontainerfactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.consumerfactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.defaultkafkaconsumerfactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.listener.concurrentmessagelistenercontainer;
import org.springframework.kafka.listener.containerproperties;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.jsondeserializer;
import java.util.hashmap;
import java.util.map;
/**
* kafka配置,也可以写在yml,这个文件会覆盖yml
*/
@springbootconfiguration
public class kafkaconsumerconfig {
@value("${spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers}")
private string bootstrapservers;
@value("${spring.kafka.consumer.group-id}")
private string groupid;
@value("${spring.kafka.consumer.enable-auto-commit}")
private boolean enableautocommit;
@value("${spring.kafka.properties.session.timeout.ms}")
private string sessiontimeout;
@value("${spring.kafka.properties.max.poll.interval.ms}")
private string maxpollintervaltime;
@value("${spring.kafka.consumer.max-poll-records}")
private string maxpollrecords;
@value("${spring.kafka.consumer.auto-offset-reset}")
private string autooffsetreset;
@value("${spring.kafka.listener.concurrency}")
private integer concurrency;
@value("${spring.kafka.listener.missing-topics-fatal}")
private boolean missingtopicsfatal;
@value("${spring.kafka.listener.poll-timeout}")
private long polltimeout;
@bean
public map<string, object> consumerconfigs() {
map<string, object> propsmap = new hashmap<>(16);
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.bootstrap_servers_config, bootstrapservers);
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.group_id_config, groupid);
//是否自动提交偏移量,默认值是true,为了避免出现重复数据和数据丢失,可以把它设置为false,然后手动提交偏移量
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.enable_auto_commit_config, enableautocommit);
//自动提交的时间间隔,自动提交开启时生效
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.auto_commit_interval_ms_config, "2000");
//该属性指定了消费者在读取一个没有偏移量的分区或者偏移量无效的情况下该作何处理:
//earliest:当各分区下有已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;无提交的offset时,从头开始消费分区的记录
//latest:当各分区下有已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;无提交的offset时,消费新产生的该分区下的数据(在消费者启动之后生成的记录)
//none:当各分区都存在已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;只要有一个分区不存在已提交的offset,则抛出异常
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.auto_offset_reset_config, autooffsetreset);
//两次poll之间的最大间隔,默认值为5分钟。如果超过这个间隔会触发rebalance
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.max_poll_interval_ms_config, maxpollintervaltime);
//这个参数定义了poll方法最多可以拉取多少条消息,默认值为500。如果在拉取消息的时候新消息不足500条,那有多少返回多少;如果超过500条,每次只返回500。
//这个默认值在有些场景下太大,有些场景很难保证能够在5min内处理完500条消息,
//如果消费者无法在5分钟内处理完500条消息的话就会触发rebalance,
//然后这批消息会被分配到另一个消费者中,还是会处理不完,这样这批消息就永远也处理不完。
//要避免出现上述问题,提前评估好处理一条消息最长需要多少时间,然后覆盖默认的max.poll.records参数
//注:需要开启batchlistener批量监听才会生效,如果不开启batchlistener则不会出现rebalance情况
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.max_poll_records_config, maxpollrecords);
//当broker多久没有收到consumer的心跳请求后就触发rebalance,默认值是10s
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.session_timeout_ms_config, sessiontimeout);
//序列化(建议使用json,这种序列化方式可以无需额外配置传输实体类)
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.key_deserializer_class_config, jsondeserializer.class);
propsmap.put(consumerconfig.value_deserializer_class_config, jsondeserializer.class);
return propsmap;
}
@bean
public consumerfactory<object, object> consumerfactory() {
//配置消费者的 json 反序列化的可信赖包,反序列化实体类需要
try(jsondeserializer<object> deserializer = new jsondeserializer<>()) {
deserializer.trustedpackages("*");
return new defaultkafkaconsumerfactory<>(consumerconfigs(), new jsondeserializer<>(), deserializer);
}
}
@bean
public kafkalistenercontainerfactory<concurrentmessagelistenercontainer<object, object>> kafkalistenercontainerfactory() {
concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory<object, object> factory = new concurrentkafkalistenercontainerfactory<>();
factory.setconsumerfactory(consumerfactory());
//在侦听器容器中运行的线程数,一般设置为 机器数*分区数
factory.setconcurrency(concurrency);
//消费监听接口监听的主题不存在时,默认会报错,所以设置为false忽略错误
factory.setmissingtopicsfatal(missingtopicsfatal);
//自动提交关闭,需要设置手动消息确认
factory.getcontainerproperties().setackmode(containerproperties.ackmode.manual_immediate);
factory.getcontainerproperties().setpolltimeout(polltimeout);
//设置为批量监听,需要用list接收
//factory.setbatchlistener(true);
return factory;
}
}
5、注解消费示例
5.1、简单消费
/**
* 指定一个消费者组,一个主题主题。
* @param record
*/
@kafkalistener(topics = iphone_topic,groupid = apple_group)
public void simpleconsumer(consumerrecord<string, string> record) {
system.out.println("进入simpleconsumer方法");
system.out.printf(
"分区 = %d, 偏移量 = %d, key = %s, 内容 = %s,创建消息的时间戳 =%d%n",
record.partition(),
record.offset(),
record.key(),
record.value(),
record.timestamp()
);
}
5.2、监听多个主题
/**
* 指定多个主题。
*
* @param record
*/
@kafkalistener(topics = {iphone_topic,ipad_topic},groupid = apple_group)
public void topics(consumerrecord<string, string> record) {
system.out.println("进入topics方法");
system.out.printf(
"主题 = %s,分区 = %d, 偏移量 = %d, key = %s, 内容 = %s,创建消息的时间戳 =%d%n",
record.topic(),
record.partition(),
record.offset(),
record.key(),
record.value(),
record.timestamp()
);
}
5.3、监听一个主题,指定分区消费
/**
* 监听一个主题,且指定消费主题的哪些分区。
* 参数详解:消费者组=apple_group;监听主题=iphonetopic;只消费的分区=1,2;消费者数量=2
* @param record
*/
@kafkalistener(
groupid = apple_group,
topicpartitions = {
@topicpartition(topic = iphone_topic, partitions = {"1", "2"})
},
concurrency = "2"
)
public void consumebypattern(consumerrecord<string, string> record) {
system.out.println("consumebypattern");
system.out.printf(
"主题 = %s,分区 = %d, 偏移量 = %d, key = %s, 内容 = %s,创建消息的时间戳 =%d%n",
record.topic(),
record.partition(),
record.offset(),
record.key(),
record.value(),
record.timestamp()
);
}
5.4、指定多个分区,指定起始偏移量,多线程消费
/**
* 指定多个分区从哪个偏移量开始消费。
* 10个线程,也就是10个消费者
*/
@kafkalistener(
groupid = apple_group,
topicpartitions = {
@topicpartition(
topic = ipad_topic,
partitions = {"0","1"},
partitionoffsets = {
@partitionoffset(partition = "2", initialoffset = "10"),
@partitionoffset(partition = "3", initialoffset = "0"),
}
)
},
concurrency = "10"
)
public void consumebypartitionoffsets(consumerrecord<string, string> record) {
system.out.println("consumebypartitionoffsets");
system.out.printf(
"主题 = %s,分区 = %d, 偏移量 = %d, key = %s, 内容 = %s,创建消息的时间戳 =%d%n",
record.topic(),
record.partition(),
record.offset(),
record.key(),
record.value(),
record.timestamp()
);
}
5.5、监听多个主题,指定多个分区,指定起始偏移量
/**
* 指定多个主题。参数详解如上面的方法。
* @param record
*/
@kafkalistener(
groupid = apple_group,
topicpartitions = {
@topicpartition(topic = iphone_topic, partitions = {"1", "2"}),
@topicpartition(topic = ipad_topic, partitions = "1",
partitionoffsets = @partitionoffset(partition = "0", initialoffset = "5"))
},
concurrency = "4"
)
public void topics2(consumerrecord<string, string> record) {
system.out.println("topics2");
system.out.printf(
"主题 = %s,分区 = %d, 偏移量 = %d, key = %s, 内容 = %s,创建消息的时间戳 =%d%n",
record.topic(),
record.partition(),
record.offset(),
record.key(),
record.value(),
record.timestamp()
);
}
5.6、指定多个监听器
/**
* 指定多个消费者组。参数详解如上面的方法。
*
* @param record
*/
@kafkalisteners({
@kafkalistener(
groupid = apple_group,
topicpartitions = {
@topicpartition(topic = iphone_topic, partitions = {"1", "2"}),
@topicpartition(topic = ipad_topic, partitions = "1",
partitionoffsets = @partitionoffset(partition = "0", initialoffset = "5"))
},
concurrency = "3"
),
@kafkalistener(
groupid = xm_group,
topicpartitions = {
@topicpartition(topic = xmphone_topic, partitions = {"1", "2"}),
@topicpartition(topic = xmpad_topic, partitions = "1",
partitionoffsets = @partitionoffset(partition = "0", initialoffset = "5"))
},
concurrency = "3"
)
}
)
public void groupids(consumerrecord<string, string> record) {
system.out.println("groupids");
system.out.println("内容:" + record.value());
system.out.println("分区:" + record.partition());
system.out.println("偏移量:" + record.offset());
system.out.println("创建消息的时间戳:" + record.timestamp());
}
5.7、手动提交偏移量
/**
* 设置手动提交偏移量
*
* @param record
*/
@kafkalistener(
topics = iphone_topic,
groupid = apple_group,
//3个消费者
concurrency = "3"
)
public void setcommittype(consumerrecord<string, string> record, acknowledgment ack) {
system.out.println("setcommittype");
system.out.println("内容:" + record.value());
system.out.println("分区:" + record.partition());
system.out.println("偏移量:" + record.offset());
system.out.println("创建消息的时间戳:" + record.timestamp());
ack.acknowledge();
}
您想发表意见!!点此发布评论


发表评论